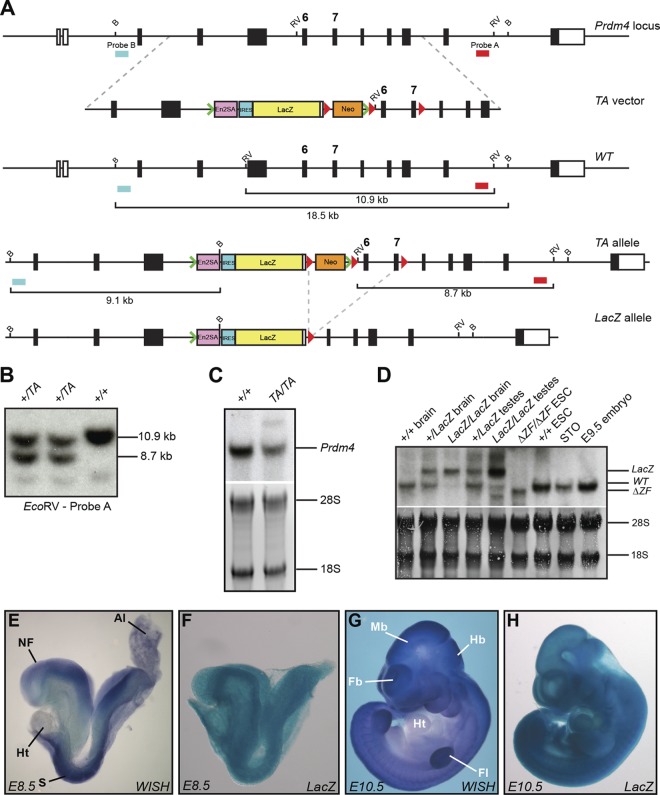
Fig 9.
Generation of Prdm4EUCOMM targeted alleles. (A) Schematic representation of the wild-type locus, targeting vector, Prdm4TA, and Prdm4LacZ deletion allele. Southern blot screening probes are indicated. B, BglII; RV, EcoRV. LoxP sites are represented by red arrowheads, and FLP recombination target (FRT) sites are represented by green arrowheads. (B) Southern blot analysis of representative drug-resistant Prdm4TA colonies. The positions of diagnostic wild-type (10.9-kb) and targeted (8.7-kb) fragments are shown. (C) Northern blot analysis of wild-type and Prdm4TA/TA adult tissues shows the production of reduced levels of wild-type Prdm4 transcripts in homozygous tissue resulting from splicing around the SA-LacZ cassette. (D) Northern blot analysis of wild-type, heterozygous, and homozygous Prdm4LacZ mouse tissue shows that Cre excision of the Neo cassette and deletion of exons 6 and 7 result in the generation of a long Prdm4 transcript incorporating the lacZ cassette. The full-length and mutated RNA fragments are indicated. Prdm4ΔZF/ΔZF ESCs, wild-type ESCs, E9.5 embryo, and STO fibroblast RNAs were also included as controls. (E to H) LacZ and whole-mount ISH (WISH) staining of Prdm4+/TA and wild-type E8.5 and E10.5 embryos shows that LacZ staining faithfully recapitulates endogenous Prdm4 staining. Abbreviations: NF, neural fold; Al, allantois; Ht, heart; S, somite; Fb, forebrain; Mb, midbrain; Hb, hindbrain; Fl, forelimb.