Fig 1.
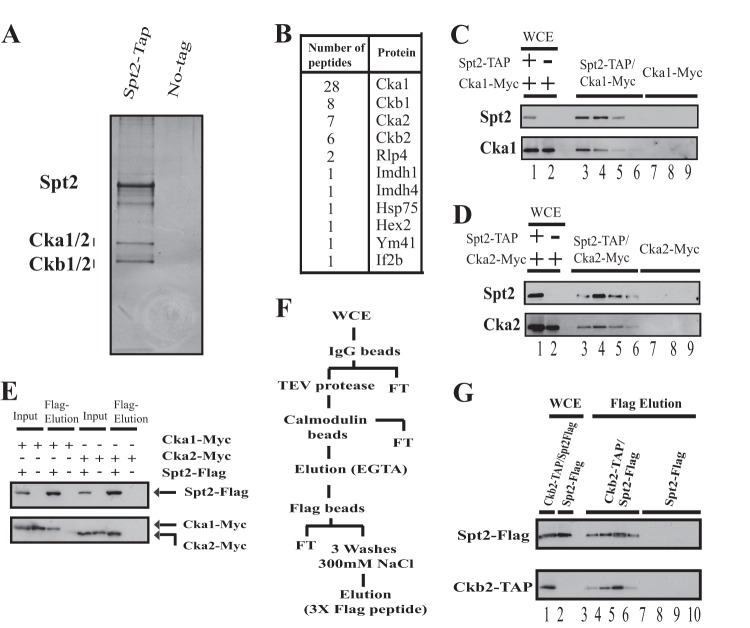
Spt2 associates stably with CK2. (A) Silver-stained gel of a TAP-purified Spt2 preparation. The right lane of the silver-stained gel is a mock purification performed with a whole-cell extract (WCE) of an untagged strain. (B) Protein bands excised from the Spt2 TAP purification gel were subjected to mass spectrometry, and the peptides identified are shown. (C and D) TAP of Spt2 from a strain expressing Spt2-TAP and Cka1-Myc or Cka2-Myc. A mock purification was performed by using a WCE of an untagged strain expressing either Cka1-Myc or Cka2-Myc. Different fractions were analyzed by Western blotting using anti-TAP and anti-Myc antibodies. (E) WCEs from cells expressing Spt2-Flag and Cka1-Myc or Cka2-Myc were immunoprecipitated with an anti-Flag antibody. The bound proteins were subsequently eluted from the anti-Flag beads with Flag peptide. A mock purification was also performed by using a WCE of an untagged strain expressing either Cka1-Myc or Cka2-Myc. The proteins eluted by the Flag peptide were analyzed by Western blotting using anti-Myc and anti-Flag antibodies. (F) Diagram illustrating the purification protocol where TAP of Ckb2 from a strain expressing Spt2-Flag and Ckb2-TAP was followed by Flag bead purification and a final Flag peptide elution. A mock purification was performed by using a WCE of an untagged strain expressing only Spt2-Flag. FT, flowthrough. (G) Different fractions from the Ckb2-TAP/Flag purification and mock purification were analyzed by Western blotting using anti-TAP and anti-Flag antibodies.