Fig 2.
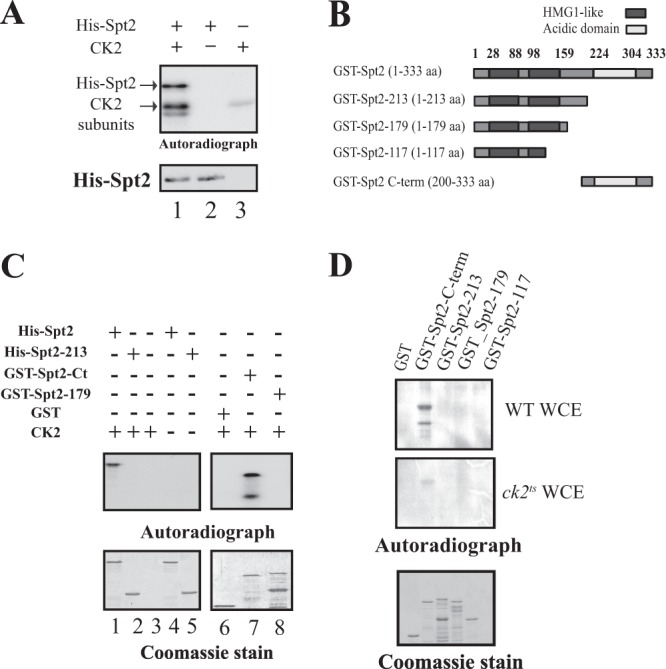
CK2 phosphorylates Spt2 in vitro on the essential C-terminal domain. (A) Yeast CK2 phosphorylates Spt2 in vitro. Recombinant His-Spt2 was incubated with TAP-purified CK2 (lane 1) or with a mock TAP purification in the presence of radiolabeled ATP (lane 2). Lane 3 shows a control kinase reaction without recombinant His-Spt2. The samples were resolved by SDS-PAGE followed by a transfer onto nitrocellulose membranes for antihistidine Western blotting or autoradiography. (B) Diagram indicating the different parts of Spt2 that were fused to GST and used in the kinase assay shown in subsequent panels. (C) Yeast CK2 modifies the Spt2 C-terminal domain in vitro. Kinase assays were performed by using TAP-purified CK2, radiolabeled ATP, and an equal amount of recombinant His-Spt2 (aa 1 to 333) (lanes 1 and 4) and the His-Spt2 N-terminal domain (aa 1 to 213) (lanes 2 and 5) or GST fused to the Spt2 N-terminal domain (aa 1 to 179) (lane 8) and to the Spt2 C-terminal domain (aa 200 to 300) (lane 7). Control reactions were carried out without recombinant proteins (lane 3), in the absence of CK2 (lanes 4 and 5), or by using purified recombinant GST (lane 6). The samples were then resolved by SDS-PAGE followed by Coomassie staining (bottom) or autoradiography (top). (D) CK2 is the major yeast Spt2 C-terminal kinase. Wild-type (WT) and ck2ts cells were grown at the permissive temperature (30°C) to mid-log phase and subsequently shifted to the restrictive temperature (37°C) for 2 h. Equal amounts of WCEs prepared from these cells were incubated with 1 μg of recombinant GST or GST fused to the indicated portion of Spt2. After GST pulldowns were performed, the beads were incubated with radiolabeled ATP. The different samples were then resolved by SDS-PAGE followed by Coomassie staining (bottom) or autoradiography (top).
