Fig 8.
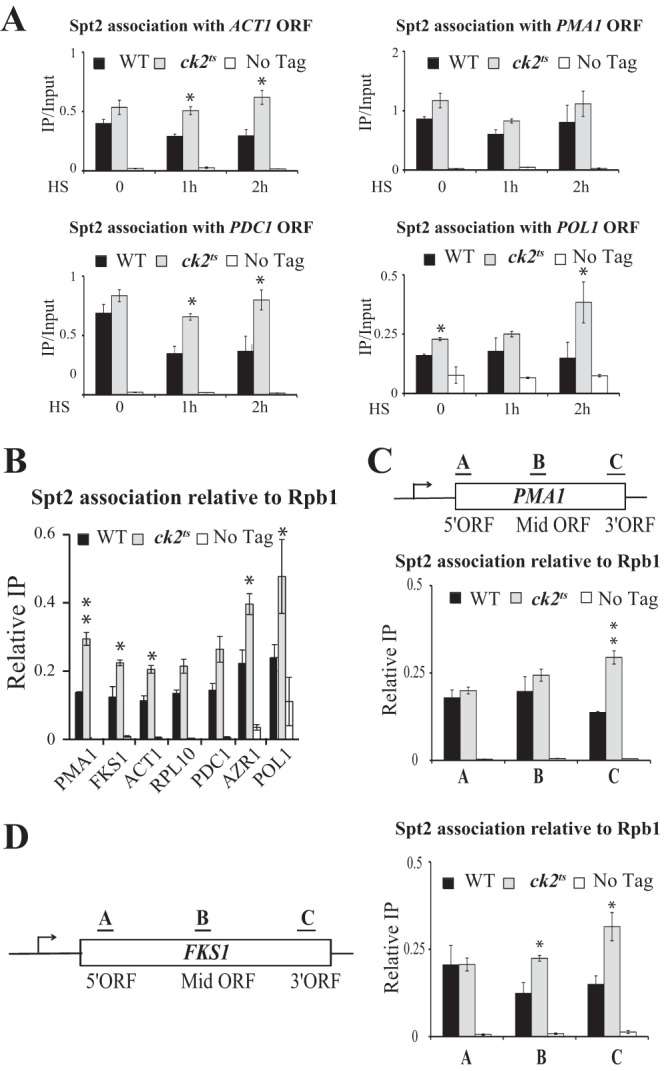
Phosphorylation by CK2 inhibits Spt2 association with chromatin. (A) CK2 depletion is associated with an increased association of Spt2 with coding regions of genes. Shown are data for ChIP assays for Spt2-13Myc. The coding regions of ACT1, PMA1, PDC1, and POL1 were analyzed by quantitative PCR. The values shown (IP/Input) represent the averages and standard errors of three independent experiments. HS, heat shock. (B) CK2 controls Spt2 recruitment to coding regions of genes independently of the transcription level. ChIP assays of Spt2-13Myc and Rpb1 were performed with chromatin extracted from wild-type, ck2ts, or untagged cells grown in yeast extract-peptone-dextrose to mid-log phase at 30°C. For each strain, the value shown represents the ratio of the percent immunoprecipitated with anti-Myc relative to the percent immunoprecipitated with anti-Rpb1 for three independent experiments. The asterisks indicate P values of <0.05. (C and D) CK2 inhibits the association of Spt2 with the 3′ ends of genes. ChIP assays of Spt2-13Myc and Rpb1 were performed as described above for panel B. The bars labeled A to C in each diagram represent the regions assayed by PCR for each gene. As in panel B, the relative Spt2 association (Relative IP) represents the ratio of the percent immunoprecipitated with anti-Myc relative to the percent immunoprecipitated with anti-Rpb1 for three independent experiments.
