Fig 6.
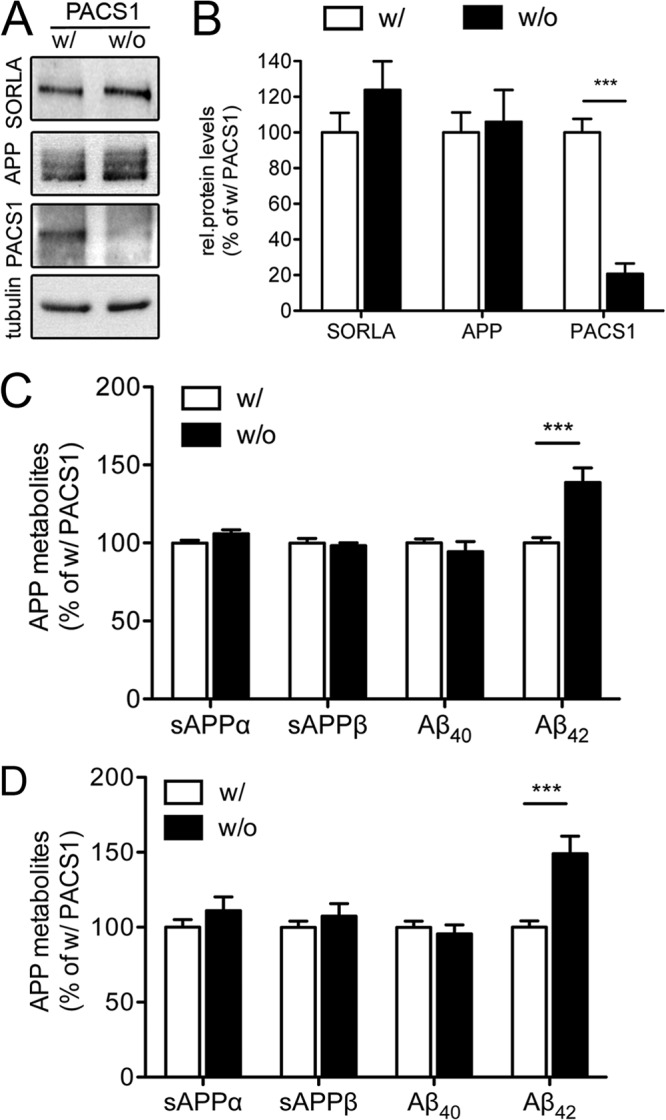
Effect of PACS1 knockdown on APP processing in SY5Y cells expressing a trafficking-defective mutant form of SORLA. (A and B) SY5Y-A/SΔCD mutant cells were treated with a siRNA directed against endogenous PACS1 (without [w/o] PACS1) or with a scrambled control siRNA (with [w/] PACS1). Western blot analysis of representative cell lysates (A) and densitometric scanning of replicate blots (B) document significant reduction of PACS1 levels in siRNA-treated SY5Y-A/SΔCD cells (number of samples per condition, 7). Levels of SORLA, APP, and tubulin (loading control) are not affected by PACS1 knockdown. rel., relative. (C) Levels of soluble APPα (sAPPα), sAPPβ, Aβ40, and Aβ42 were determined by ELISA in SY5Y-A/SΔCD cells treated with a siRNA directed against PACS1 (without PACS1 [w/o]) or with a scrambled control siRNA (with PACS1 [w/]). Data are the means ± the standard errors of the means of triplicate measurements in five independent experiments. Values were calculated as percentage of the scrambled siRNA control (with PACS1, set to 100%). (D) Same as panel C but with an alternative siRNA directed against PACS1 as described in Materials and Methods. Data represent the means ± the standard errors of the means of triplicate measurements of four independent experiments (***, P < 0.001).
