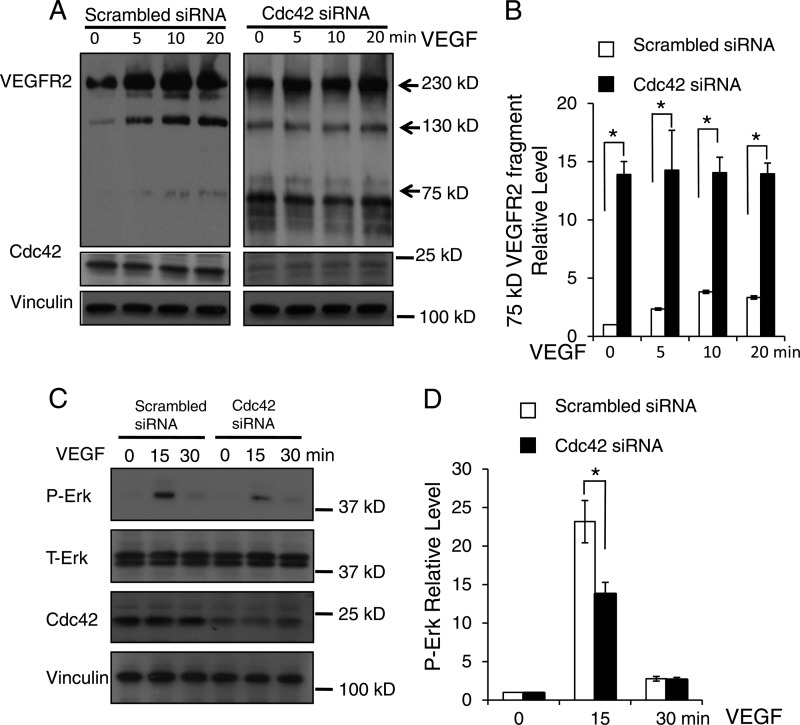
Fig 11.
Inactivation of Cdc42 promoted VEGFR2 shedding and impaired VEGF-induced Erk phosphorylation. (A) HUVECs were transfected with either scrambled siRNA (left) or Cdc42-targeted siRNA (right) and were then labeled with biotin. After treatment with 50 ng/ml VEGF from 0 to 20 min, the biotin tags on the cell surface were removed by l-glutathione (reduced), and the internalized biotin-labeled proteins were analyzed by Western blotting with anti-VEGFR2 antibodies. Full-length VEGFR2 (230 kDa) and the smaller VEGFR2 fragments detected (130 kDa and 75 kDa) are indicated by arrows. Cdc42 expression was assessed to confirm the efficiency of siRNA treatment against Cdc42, and vinculin was utilized as a loading control. (B) Quantitative analysis shows that Cdc42 knockdown significantly increased the production of the 75-kDa VEGFR2 fragment. *, P < 0.05. (C) HUVECs were transfected with scrambled siRNA or Cdc42 siRNA and were challenged with VEGF at the indicated time points. Whole-cell lysates were analyzed by Western blotting with specific antibodies against phosphorylated Erk (P-Erk) and total Erk (T-Erk). (D) Quantitative data show that Cdc42 knockdown significantly decreased the P-Erk level in response to VEGF stimulation at 15 min.