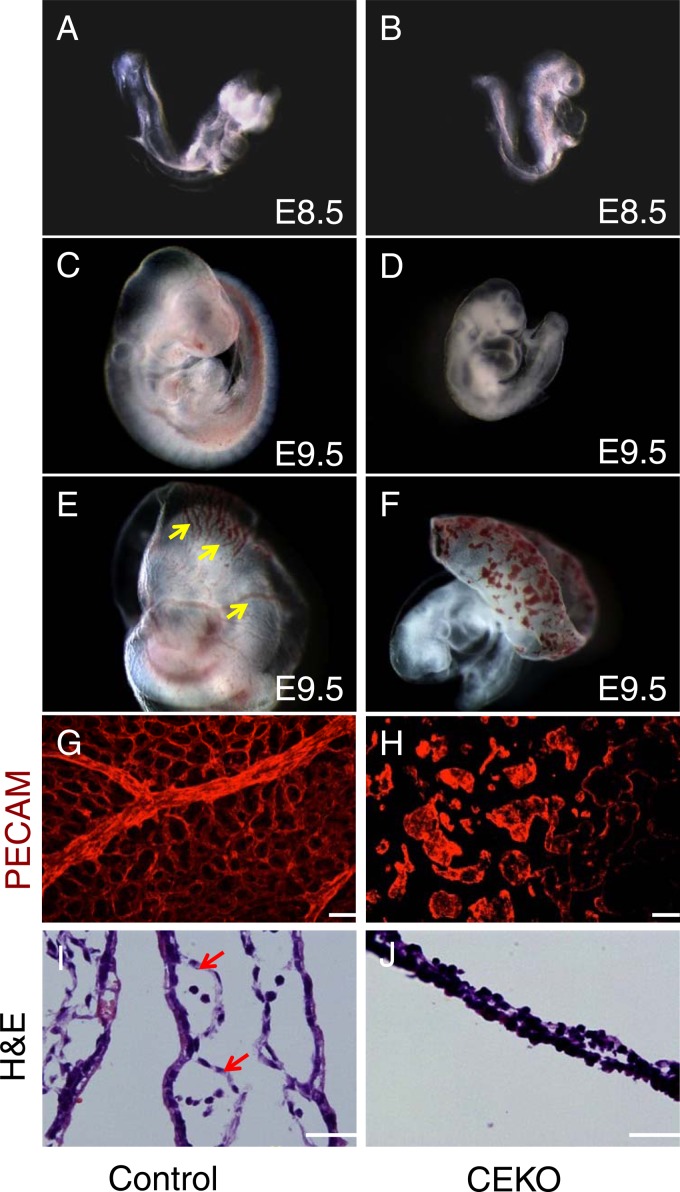
Fig 2.
Deletion of Cdc42 in vascular ECs caused vasculogenesis defects in the yolk sac. (A through D) Gross examination of E8.5 control (A) and CEKO (B) embryos showed similar morphologies. Side views of E9.5 control (C) and CEKO (D) embryos revealed that CEKO embryos had smaller bodies. (E and F) The control E9.5 yolk sac presented highly organized vasculature (arrows) (E), but only the blood islands were evident in the yolk sacs of CEKO embryos (F). (G and H) Whole-mount staining with PECAM-1 performed on the yolk sacs of control (G) and CEKO (H) embryos. (I and J) Hematoxylin- and eosin-stained sections of yolk sacs from control (I) and CEKO (J) embryos. Arrows indicate blood vessels in the yolk sacs. Bars, 25 μm.