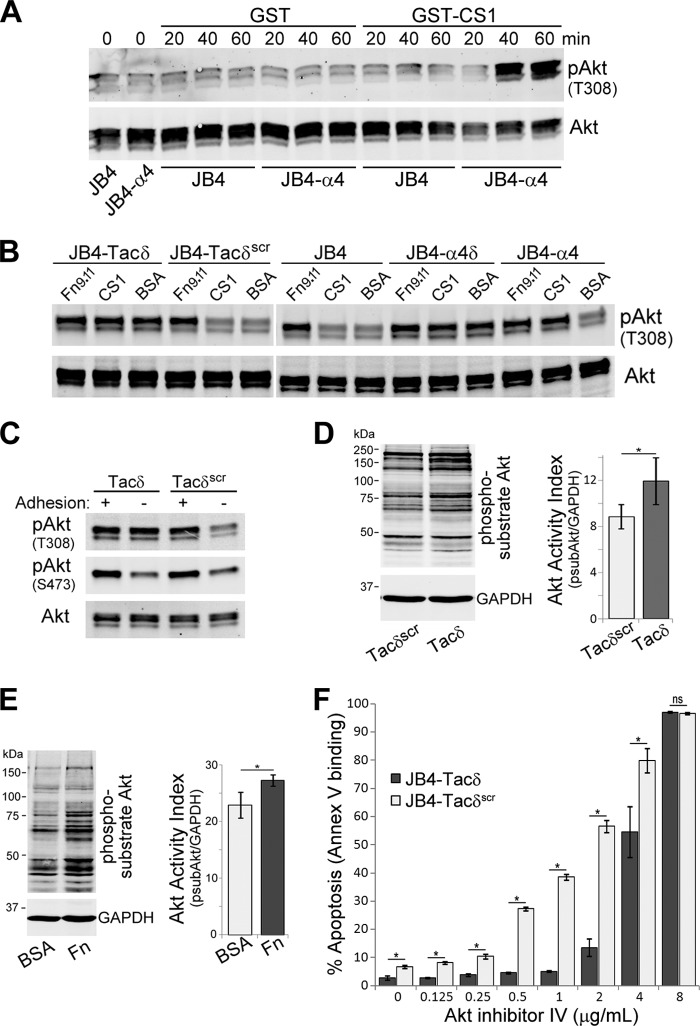
Fig 4.
α4δ and Tacδ expression circumvents the requirement for cell adhesion-mediated stimulation of Akt phosphorylation and activation. (A) JB4 or JB4-α4 cells were plated on dishes coated with GST-CS1 or GST for the indicated times, and cell lysates were immunoblotted to detect T308-phosphorylated Akt (pAkt) and total Akt levels. (B) JB4-Tacδ, JB4-Tacδscr, JB4, JB4-α4δ, and JB4-α4 cells were plated on dishes coated with GST-CS1, GST-Fn9.11, or BSA for 45 min, and cell lysates were immunoblotted to detect pAkt and total Akt levels. (C) JB4-Tacδ and JB4-Tacδscr cells were plated on dishes coated with GST-Fn9.11 (adhesion +ve) or GST (adhesion -ve) for 45 min, and cell lysates were immunoblotted to detect T308- or S473-phosphorylated Akt (pAkt) and total Akt levels. (D) Lysates of JB4-Tacδ and JB4-Tacδscr cells were blotted to detect Akt-phosphorylated substrates and GAPDH. The Akt activation index was calculated as the total fluorescence of Akt-phosphorylated substrates divided by GAPDH activity (means ± standard deviations; 3 independent experiments). *, P < 0.05. (E) Lysates of Jurkat cells plated on dishes coated with BSA or fibronectin for 30 min were blotted to detect Akt-phosphorylated substrates and GAPDH as described for panel D. Data are plotted as the Akt activation index (means ± standard deviations; 3 independent experiments). *, P < 0.03. (F) JB4-Tacδ and JB4-Tacδscr cells were treated with Akt inhibitor IV at the indicated concentrations for 48 h. Data are plotted as the percentage of apoptotic cells, based on flow cytometry determination of Cy5-annexin V binding (means ± standard deviations; n = 3). *, P < 0.02; ns, not significant.