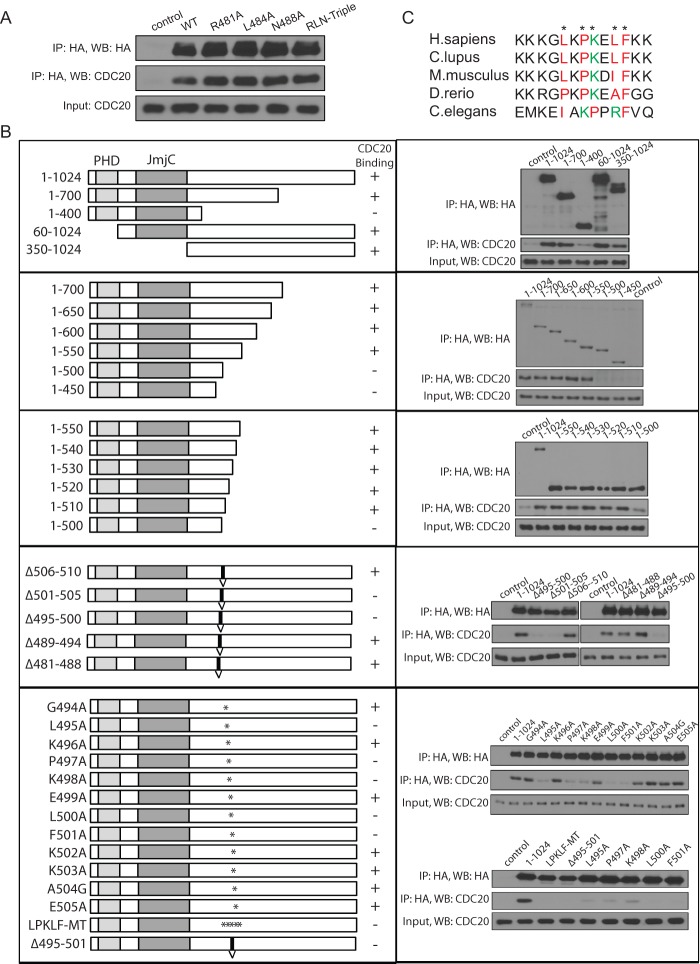
Fig 3.
A novel motif on PHF8 governs its binding to CDC20. (A) The D-box motif on PHF8 was mutated in Flag-HA-PHF8 to generate mutants with an R481A, L484A, or N488A mutation or the RLN-Triple mutant (R481A L484A N488A triple mutant). The empty vector, wild-type (WT) Flag-HA-PHF8, or the various mutants were transfected in HEK293T cells, and lysates were used for HA IP and immunoblotted for CDC20. (B) Deletion mutants of Flag-HA-PHF8 were generated to map the CDC20 binding region. In the left column, constructs are shown with respect to the PHD domain and JmjC domain. Constructs were first cut at the N or C terminus (first three panels) to narrow down the region needed for binding. Next, small deletions (indicated with a “V”) were generated in the full-length protein, followed by single- or multiple-point mutations (indicated with an ∗). These constructs were transfected into HEK293T cells, subjected to HA IP, and immunoblotted for CDC20. An LXPKXLF motif from aa 495 to 501 was determined to be essential for CDC20 binding to PHF8. (C) PHF8 orthologues from various species were aligned by ClusterW2 analysis, and the LXPKXLF motif (indicated with an ∗) is highlighted in color, with red indicating hydrophobic and green indicating basic amino acids. H. sapiens, Homo sapiens; C. lupus, Canis lupus; D. rerio, Danio rerio.