Figure 1.
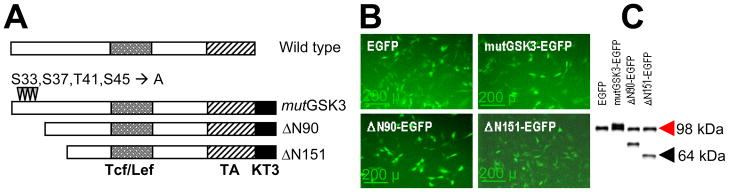
Structure and expression of β-catenin mutants. (A) Three different β-catenin mutants (mutGSK, ΔN90 and ΔN151) are shown below the basic structure of the wild type protein. The 4 phosphorylation sites (mutated to alanine in mutGSK3) at the N-terminus are shown, as well as the Tcf/Lef-binding domain (shaded), the transactivation domain (TA, hatched), and the KT3 epitope (solid). (B) C3H10T1/2 cells were transduced with VSV-G retroviruses encoding EGFP only, or a bicistronic construct comprised of one β-catenin mutant and IRES-EGFP. Fluorescence microscopy shows G418-resistant cells expressing EGFP. (C) Western analysis detects expression of the β-catenin mutant proteins in similar abundance to endogenous β-catenin (red arrowhead).
