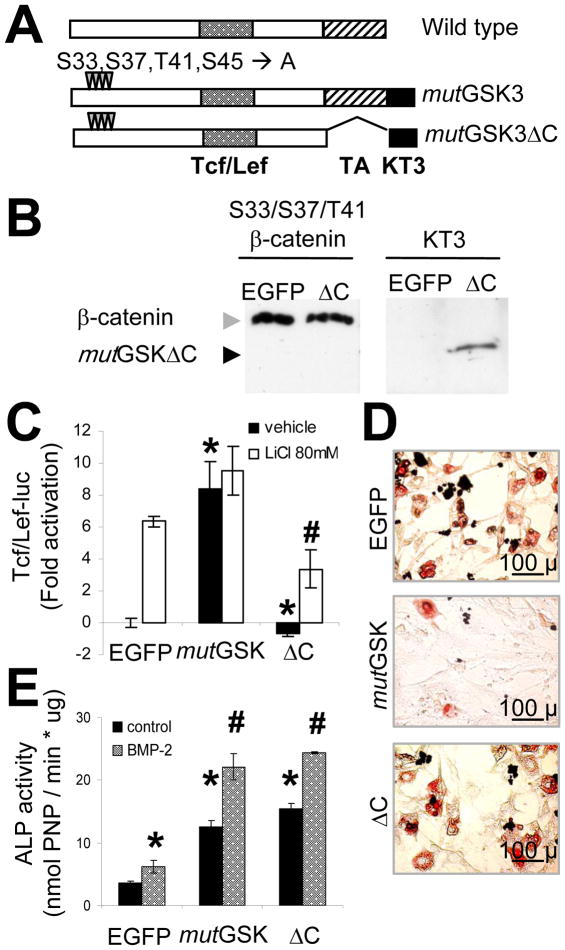
Figure 3.
The C-terminal transactivation domain of β-catenin is necessary for Tcf/Lef transcriptional activity and for suppression of adipogenesis, but is dispensable for osteogenic stimulation. (A) Schematic diagram of wild type and mutant (mutGSK, or mutGSKΔC) β-catenin constructs, with their functional domains illustrated as in Fig 1A. (B) C3H10T1/2 cells were transduced with either EGFP or mutant β-catenin (mutGSK, or mutGSKΔC) VSV-G retroviruses. Whole cell lysates were immunoblotted using either an anti-β-catenin or anti-KT3 antibody, as indicated. (C) Cells transduced with the different mutants were monitored for Tcf/Lef transcriptional activity in the absence or presence of 80 mM LiCl after transfection with Tcf/Lef-luc; p<0.05 versus EGFP (*) or versus EGFP plus LiCl (#), two-tailed Student t-test. (D) Adipogenic differentiation was determined in transduced C3H10T1/2 cells by Oil Red O staining after 10 d incubation in adipogenic medium. (E) Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity was quantified in cell lysates in the absence or presence of 100 ng/ml BMP-2 after 7 d; p<0.05 versus EGFP (*) or versus EGFP plus BMP-2 (#), two-tailed Student t-test. Results are representative of 3 separate experiments. Bar, 100 μm.