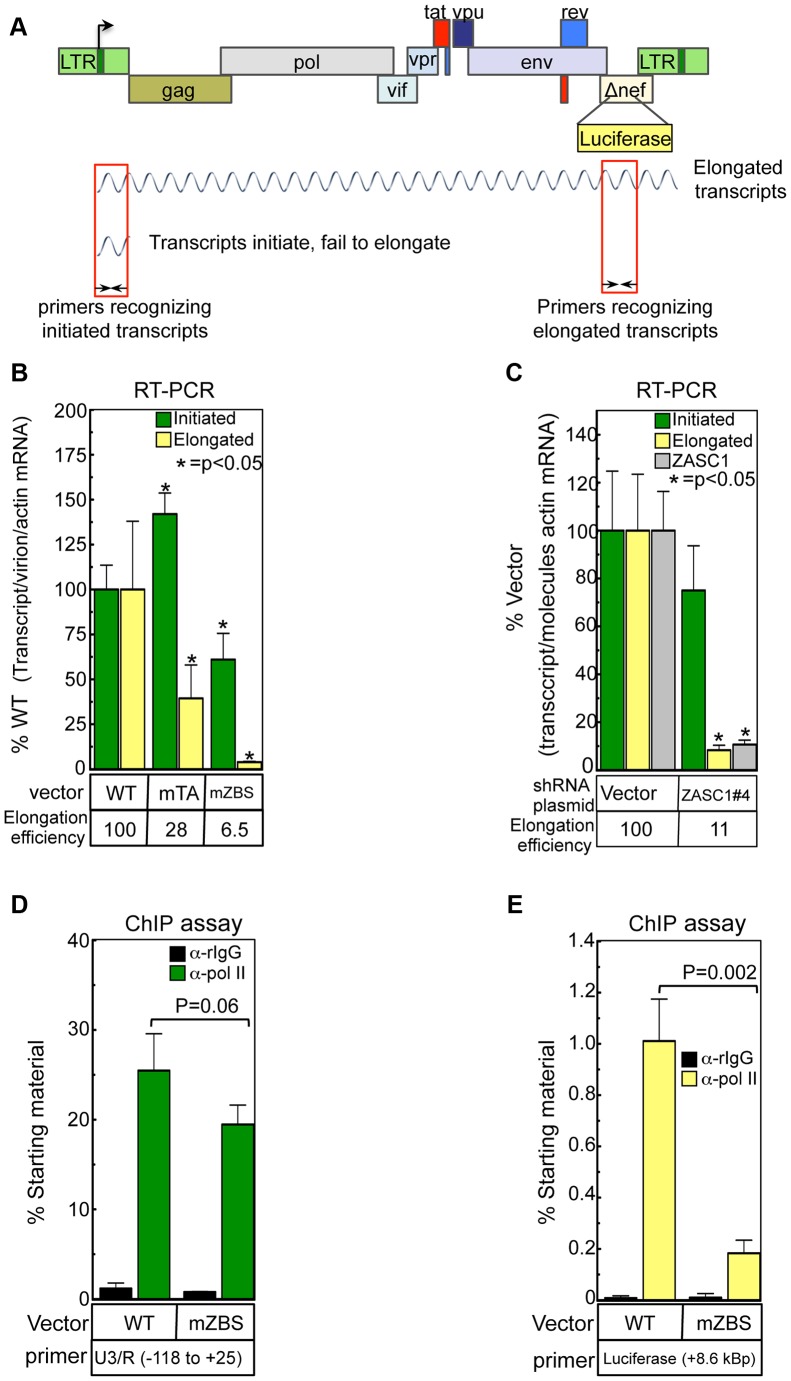
Figure 3. ZASC1 promotes HIV-1 transcription elongation.
(A) Schematic of the HIV-1 vector NL43E-R-Luc indicating the two types of primary transcripts and the PCR primers utilized to differentiate them. (B) The amount of initiated and extended transcripts was assayed in cells challenge with NL43E-R-Luc or ZBS variants by isolating total RNA 48 hpi and performing real-time reverse transcription PCR with primers that amplify all initiated transcripts (+1 to +58) or transcripts that have been initiated and extended (+9961 to +10,191). Transcript values were normalized for the amount of input virion RNA and total cellular actin mRNA. Real-time PCR was performed in triplicate. Elongation efficiency of panel B was determined by dividing the extended transcripts by the total initiated transcripts with WT efficiency set at 100%. (C) HEK293 cells (1×105) were transfected with an shRNA vector plasmid or an shRNA targeting ZASC1 (shRNA ZASC1#4, see Fig. 2B), 72 hrs post transfection, the cells were challenged with WT NL43-luc. 48 hrs post infection, total RNA was harvested and initiated and extended transcripts were analyzed and elongation efficiency determined as in B. ZASC1 RNA was analyzed as in Fig. 2B. (D) Total RNA polymerase II bound to either NL43E-R-Luc or a derivative with all ZBS mutated (Fig. 1A) was measured by chromatin immunoprecipitation assays using a primer set that spans the transcription initiation site (−116 to +25) or (E) a primer set that amplifies the luciferase gene in the nef locus approximately 9 kBp downstream from the transcription start site. Error bars indicate the standard deviation of the data and are representative of three independent experiments. P-values were calculated using a standard Student's t-test and significant changes relative to WT or relevant bracketed comparisons indicated.