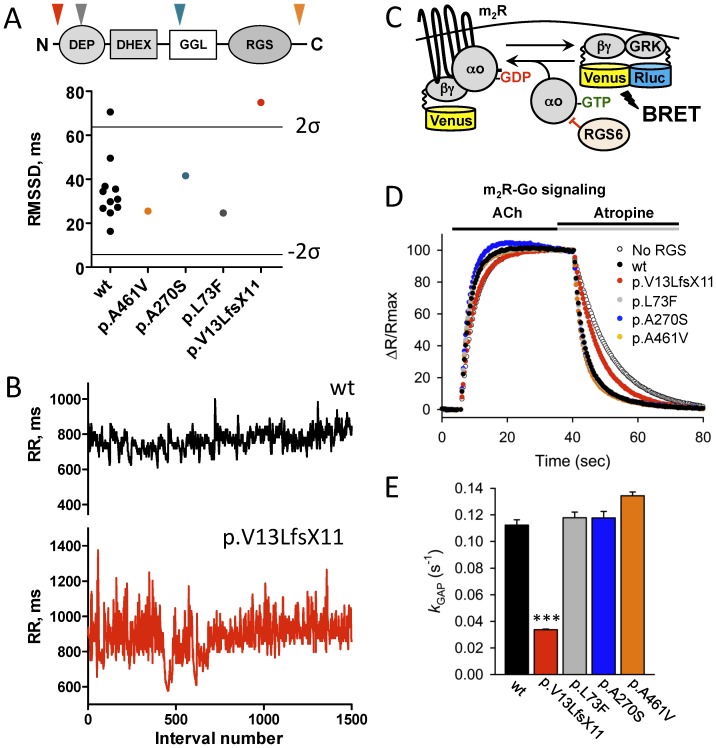
Figure 5. Abnormal sinus arrhythmia in a human subject with dysfunctional RGS6.
A, HRV measured in humans carrying variants in RGS6 and 11 age-matched control subjects (wt, black). Lines represent upper (2σ) and lower (−2 σ) 95% confidence thresholds as determined by the 2σ rule. Insert: domain structure of RGS6 protein. Arrows show localization of corresponding variants. B, Representative tachograms of RR intervals from a control subject (black) and a subject heterozygous for the p.Val13LeufsX11 variant in the RGS6 gene (red) determined from continuous Holter recordings. C, Schematics of the assay design to study effects of mutations on the RGS6 function. Stimulation of the m2R by ACh results in the dissociation of Gμo from the heterotrimer. Released Gβγ subunits tagged with Venus become available for the interaction with Nluc8-tagged GRK reporter producing the BRET signal. D. Representative responses to sequential application of ACh (10 µM) and atropine (1 mM) recorded in the presence of the indicated constructs. The BRET signals averaged from 4 experiments were plotted as individual data points. E, Catalytic activity of RGS6 defined by the k GAP parameter. To determine the k GAP values, the deactivation rate constant measured in the absence of RGS6 was subtracted from values measured in the presence of RGS6. Symbols: ***, p<0.001 (n = 4).