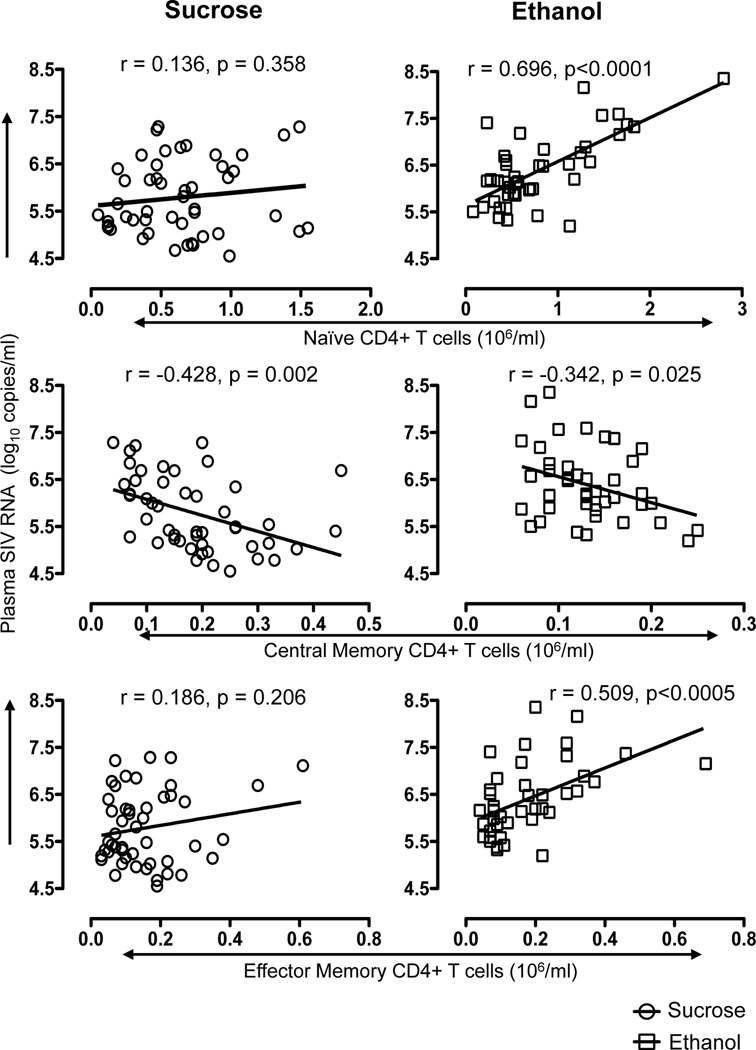
Figure 2.
Correlation between plasma viral load and different blood CD4 T-cell subsets in sucrose and ethanol treated macaques determined between 28–120 days post SIV infection. A significant positive correlation was detected between either naïve (CD28+CD95-) or effector memory (CD28-CD95+) CD4+ T-cells and plasma viral load in ethanol treated SIV infected macaques, but not sucrose treated animals. In contrast, a significant but weaker inverse correlation was observed between central memory (CD28+CD95+) CD4+ T-cells and plasma viral load in both sucrose and ethanol treated SIV infected macaques. Spearman’s nonparametric correlation was used to determine the degree of correlation in all comparisons.