Fig. 1.
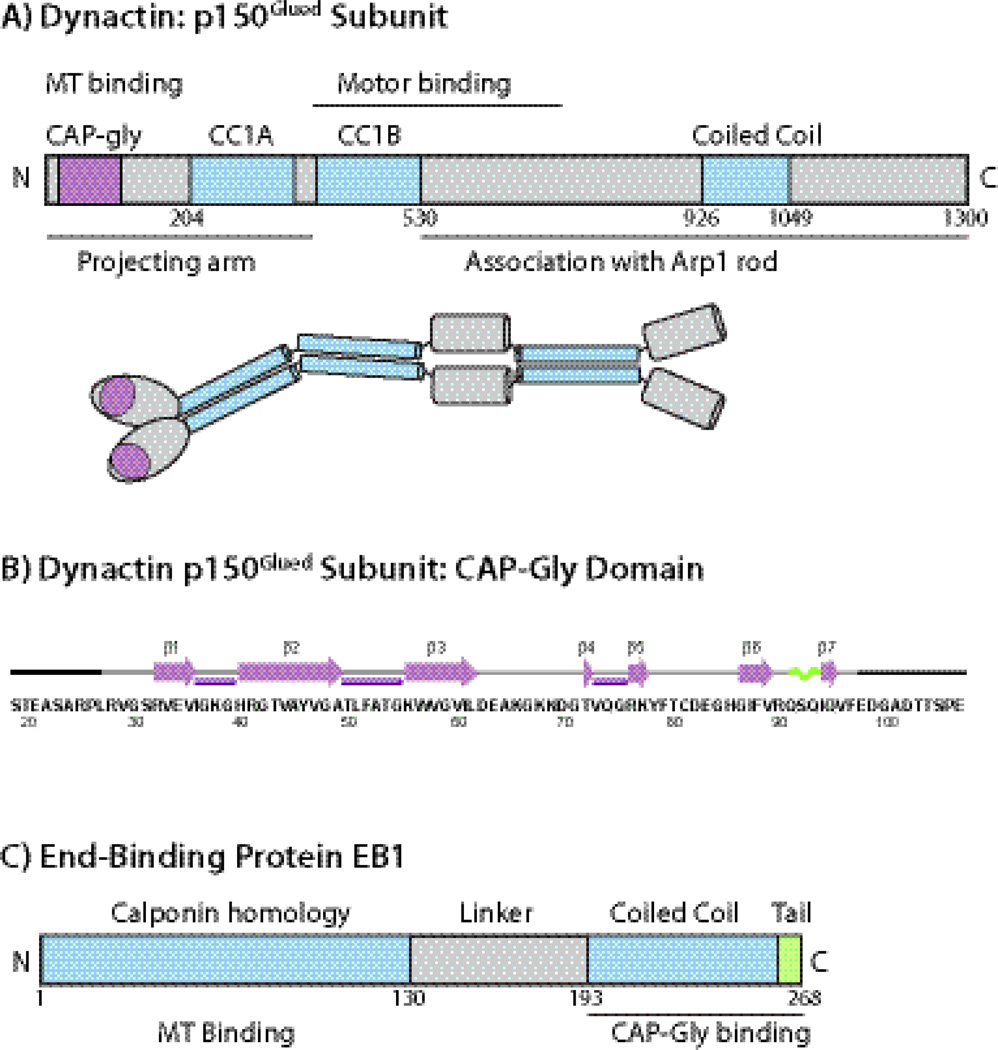
A) The domain structure and overall organization of dynactin’s p150Glued subunit. The CAP-Gly domain is located at the N-terminus of p150Glued subunit. B) Amino acid sequence and secondary structure of the CAP-Gly domain of dynactin under investigation. The secondary structures of residues L27-F97 are based on the TALOS+-derived torsion angles from solution and solid-state NMR spectroscopy and from the X-ray structures. Residues corresponding to the N-terminus (19–26) and C-terminus (98–107) do not give rise to cross peaks in the C-C correlation spectra, and were not included in the 3D structure calculation. C) The domain structure of EB1. The C-terminal dimerization domain is coiled coil with a disordered acidic tail and provides the CAP-Gly binding sites. The EB1 protein under investigation is the C-terminal domain encompassing residues 193–268.