Figure 1.
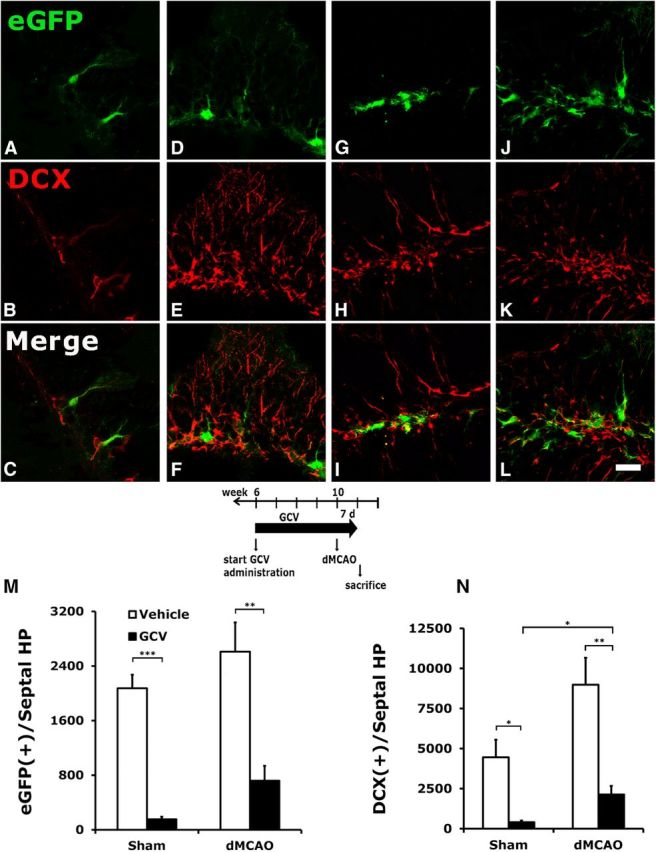
Conditional ablation of hippocampal NPCs by GCV in TK+ mice subjected to stroke or sham surgery. A–L, Vehicle or GCV was administered to TK+ mice for 4 weeks before stroke or sham surgery, and continued for 7 d after surgery until the mice were killed. Type 1 (EGFP-immunoreactive) and type 2b (DCX-immunoreactive) progenitors were significantly reduced following GCV treatment in mice who had undergone either sham surgery (A–C) or a dMCAO procedure (G–I) compared with those treated with vehicle (D–F and J–L, respectively). M, N, Although type 1 NPCs in the DG showed a tendency to increase (M) and type 2 cells had a significant increase (N) after stroke, they were still much reduced compared with the corresponding groups in the vehicle-treated mice. GCV also reduced the degree of dendritic arborization in the type 1 NPCs in the DG (G), compared with the elaborate radial process observed in the vehicle-treated EGFP cells (J). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.005. Scale bar, 25 μm. N = 3–4/group.
