Figure 7. Genetic requirements for three double strand break repair pathways in mycobacteria.
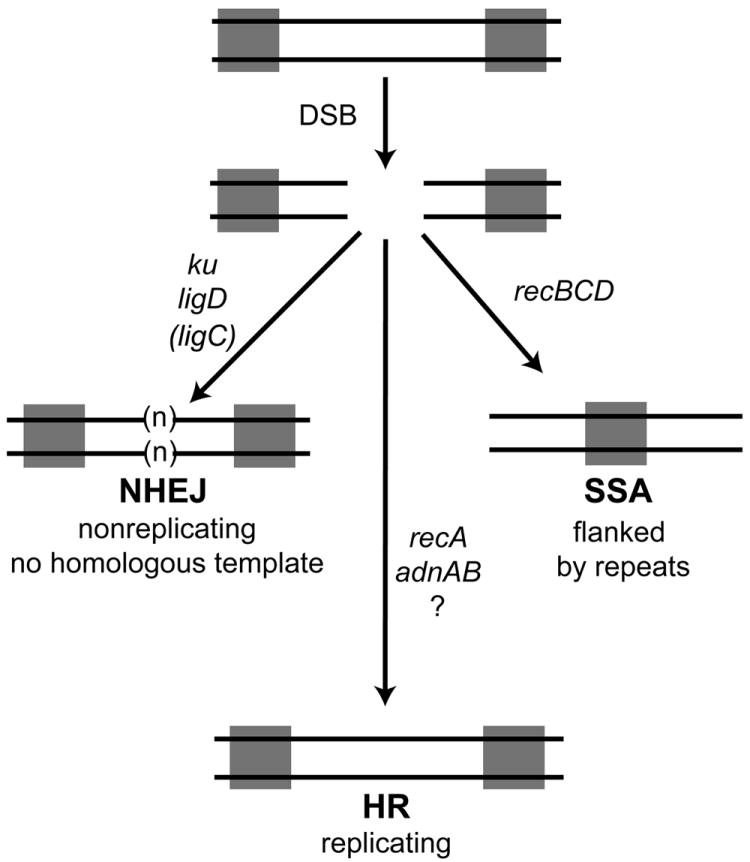
We depict a double strand break (DSB) flanked by two repeats (gray squares). The break can be repaired by NHEJ, a pathway defined by ku and ligD with a secondary role for ligC when LigD is inactivated (see Aniukwu et al., 2008). NHEJ can add additional nucleotides (n), or result in deletions into the DNA surrounding the break. NHEJ does not require a homologous template for repair and therefore can repair DSB in nonreplicating cells. Repair by HR is dependent on recA and adnAB, but is independent of recBCD. Our data indicate a additional pathway of adnAB independent, recA dependent HR (indicated by ?) evinced by the residual HR in the ΔadnAB strain. Repair by the SSA pathway is achieved by bidirectional single strand resection to reveal the complementary repeats which anneal, resulting in a deletion and retention of one copy of the repeat. Our assays indicate that the mycobacterial SSA pathway requires recBCD.
