Figure 3.
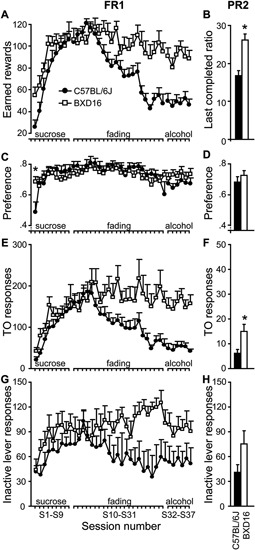
Enhanced motivation for alcohol in BXD16 mice. Under an FR1-schedule of reinforcement, (A) BXD16 mice earned a significant higher number of rewards when alcohol was added to the reward (S10-S31), which persisted until mice responded for a 10% alcohol solution (S32–S37). (B) Under a PR2 schedule of responding for 10% alcohol reward, BXD16 mice reached a higher last completed ratio than C57BL/6J. (C,D) BXD16 mice showed a faster development of dissociation of active and inactive lever compared with C57BL/6J and showed equal preference during FR1 and PR2 responding for 10% alcohol. (E,F) BXD16 showed enhanced TO responding on the active lever during FR1 and PR2 responding for 10% alcohol compared with C57BL6J. (G,H) BXD16 and C57BL/6J mice did not show a significant difference in inactive lever responding during FR1 and PR2 responding for 10%. For statistical evaluation of results, see Table 2 and text. *P < 0.05.
