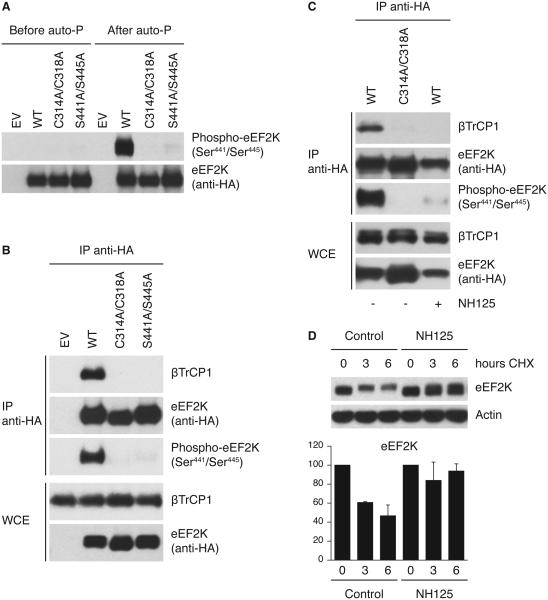
Figure 5. eEF2K autophosphorylation on the degron triggers its binding to βTrCP.
(A) In vitro autophosphorylation of the eEF2K degron. U2OS cells were transfected with either HA-tagged wild type eEF2K, eEF2K(C314A/C318A), or eEF2K(S441A/S445A). eEF2K was purified, dephosphorylated by λ-phosphatase treatment, and then allowed to autophosphorylate in vitro. Samples were then analyzed by immunoblotting. Auto-P: autophosphorylation reaction. (B) Kinase-dead eEF2K mutant does not bind βTrCP1. U2OS cells were transfected with an empty vector (EV), HA-tagged wild type eEF2K, eEF2K(C314A/C318A), or eEF2K(S441A/S445A). After transfection, cells were synchronized in G2 as described in Figure 3A, pulse-treated with doxorubicin, and collected after 8 hours. Three hours before harvesting, cells were treated with MG132. (C) The βTrCP1-eEF2K interaction is blocked by an eEF2K inhibitor. U2OS cells were transfected with an empty vector (EV) or HA-tagged eEF2K. Cells were treated as in (B) and, when indicated, treated with the eEF2K inhibitor NH125. (D) NH125 induces the stabilization of eEF2K. Cells were pulse-treated with doxorubicin and then treated with NH125. eEF2K turnover was analyzed by cycloheximide chase (100 μg/ml for indicated times). The graph illustrates the quantification of eEF2K abundance relative to the amount at time 0. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments.