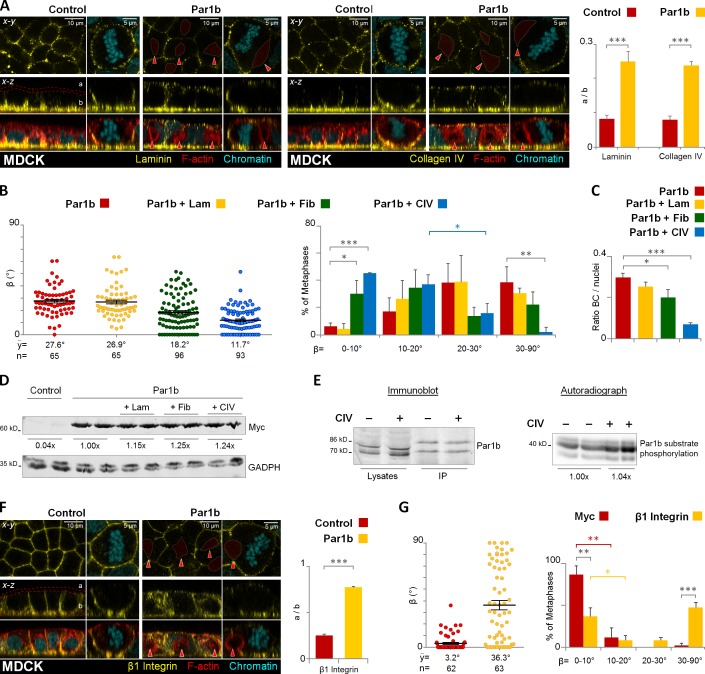
Figure 5.
Par1b regulates lumen polarity and mitotic spindle orientation in MDCK cells via ECM signaling. Control and MDCK cells overexpressing Par1b (A–E) were fixed and stained for F-actin with phalloidin-TRITC, chromatin, and either laminin, collagen IV (A), or integrin β1 (F). The distribution of the ECM proteins or the integrin β1 in the apex (a) versus base (b) in 2D cultures monolayers was quantified (A and F, right panels, respectively). MDCK-Par1b (B and C) were plated on either uncoated (Control), laminin (+Lam), fibronectin (+ Fib), or collagen IV (+ CIV) matrices. The cells were fixed and stained for gp135, α-tubulin, and chromatin (not depicted). The β angle (B) and the amount of BC-like lumina in interphase cells (C) were quantified. The percentage of (+CIV) Par1b cells with β angles between 10–20° (37.1 ± 7.1%) differed significantly from that in the 20–30° category (15.8 ± 7.3%). (D) Recombinant Par1b expression levels when MDCK-Par1b cells were plated on either plastic, laminin (+ Lam), fibronectin (+ Fib), or collagen IV (+ CIV). (E) Par1b activity in MDCK cells plated on either plastic (−) or CIV (+). Immunoblot: endogenous Par1b levels (lysates), and the immunoprecipitated fraction used for in vitro kinase assays (IP). The double band corresponds to two splice variants of Par1b. Audioradiograph: phosphorylation of a standard substrate in an IP-kinase assay. (G) MDCK cells were incubated 4 h in vivo with myc (control) or integrin β1 antibodies. Cells were fixed stained as in B. The β angle was quantified. Red arrowheads, BC-like lumina. Error bars indicate ± SEM (dot graphics) or + SD (bar graphics). *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001.