Figure 1.
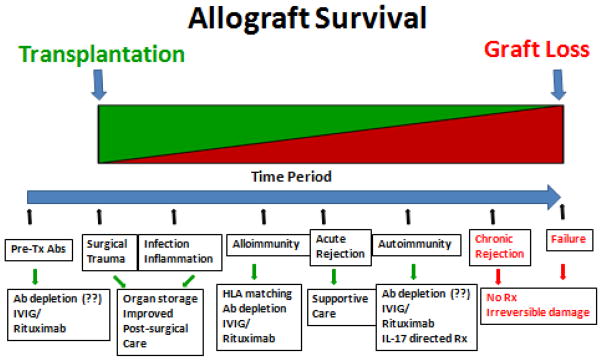
Temporal depiction of the sequence of events leading to allograft failure. The temporal sequence of initial inflammatory events following solid organ transplantation such as surgical stress, viral infections, GERD, mismatched HLA, etc leads to inflammatory injury to the allograft. These risk factors potentially play an important role in the acute rejection episode. Further, presence of pre-transplant Abs to self-antigens could also lead to higher incidence of alloimmunity and allograft rejection. This initial inflammatory injury could potentiate tissue remodeling and exposure of cryptic self-antigens and leading to autoimmunity and potential development of CR. Potential therapeutic options have been listed in the last panel. Green, indicates functioning allograft; and red, indicates non-functional allograft (color code given only for representation and not intended to indicate exact allograft survival temporal percentage).
