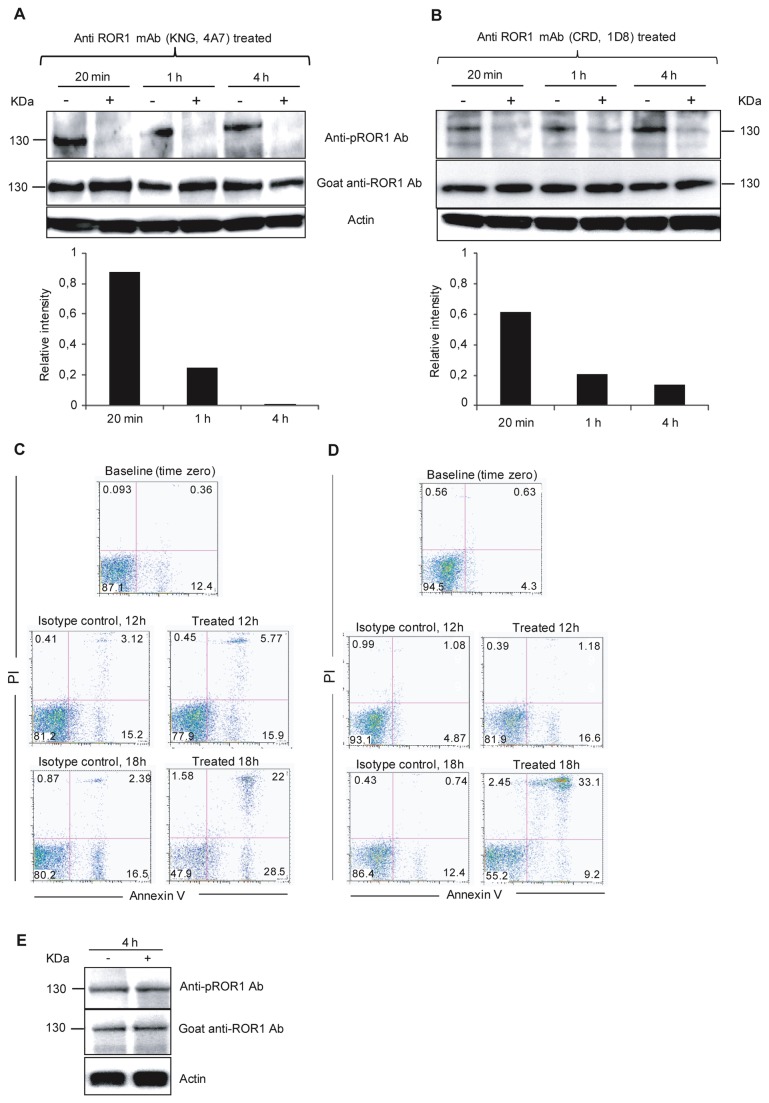
Figure 5. Anti-ROR1 mAbs induced dephosphorylation of ROR1 and subsequent apoptosis of CLL cells.
Representative experiments of time-dependent ROR1 dephosphorylation and apoptosis in vitro incubated with an anti-KNG (4A7) (A and C) and anti-CRD (1D8) (B and D) anti-ROR1 mAb respectively. Representative experiments from two progressive (CLL 5102 and CLL 5116) CLL patients are shown. Leukemic cells were incubated for 20 min, 1, 4 hours with a non-relevant IgG1 isotype control mAb (-) and the ROR1 mAbs (+). Cells were harvested and lysed for western blot experiments (A and B). The non-relevant isotype control mAb did not induce dephosphorylation of ROR1 (130 kDa) while the anti-ROR1 mAb induced dephosphorylation already after 20 min, which increased by time. The intensity of pROR1 was measured by ImageJ software. The ratio of pROR1/ROR1 intensity of treated sample to pROR1/ROR1 intensity of untreated sample (relative intensity) is shown in a histogram. A value <1 indicates dephosphorylation of ROR1 after treatment with the anti-ROR1 mAb compared to the non-relevant isotype control mAb. Apoptosis of CLL cells (Annexin V+/PI+) after 0, 12 and 18 h incubation with the anti ROR1 mAbs without the addition of immune effector cells or complement (C and D). An anti-CD20 mAb (ofatumumab) did not induce dephosphorylation of ROR1 after 4h incubation in two CLL patients. A representative experiment is shown for one of the CLL patients (E).