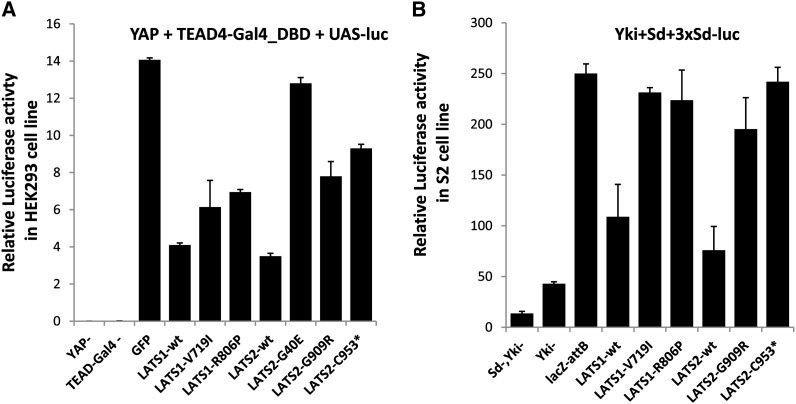
Figure 4.
Activities of hLATS1/2 and variants in regulating YAP/Yki transcriptional coactivator activity in both human and Drosophila cells. (A) Relative luciferase activity in HEK293T cells that overexpressed Renilla luciferase as an internal control, UAS-luciferase, CMV-YAP (except the first column), and fusion construct TEAD4-Gal4 that fuses TEAD4 with Gal4 DNA-binding domain (except the second column). (B) Relative luciferase activity of UAS-LATS1/2-wild type and mutants in S2 cells that overexpressed Renilla luciferase as an internal control, 3xSd (Scalloped)-luciferase, Ac-Yki (except the first and second columns), and UAS-Sd (except the first column). HEK293T cells were maintained in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium, containing 10% fetal calf serum and 0.5% penicillin–streptomycin. They were transiently transfected using PolyFect Transfection Reagent (Qiagen) and harvested 36 hr later. Plasmids include wild-type or mutant hLATS1 and hLATS2 in pcDNA3.1-Hygro-3xFLAG, pCMV-YAP, pCMV-Gal4-TEAD4, pUAS-LUC, and pCMV-Renilla (gift from Kun-Liang Guan). Cells were lysed after 36 hr and luciferase activity was detected using the Dual-Luciferase Reporter assay kit and GloMax multi detection system (Promega). Drosophila S2R+ cells were cultured in Schneider’s medium (Sigma), containing 10% fetal calf serum. S2 cells were transfected using Effectene (Qiagen) with wild-type or mutant hLATS1/2 in pUAST-attB, pAc-Yki, pUAST-Sd, p3xSd-LUC, and copia-Renilla (gift from Jin Jiang), together with pAc-Gal4. Results represent the mean of standard error of three independent experiments.