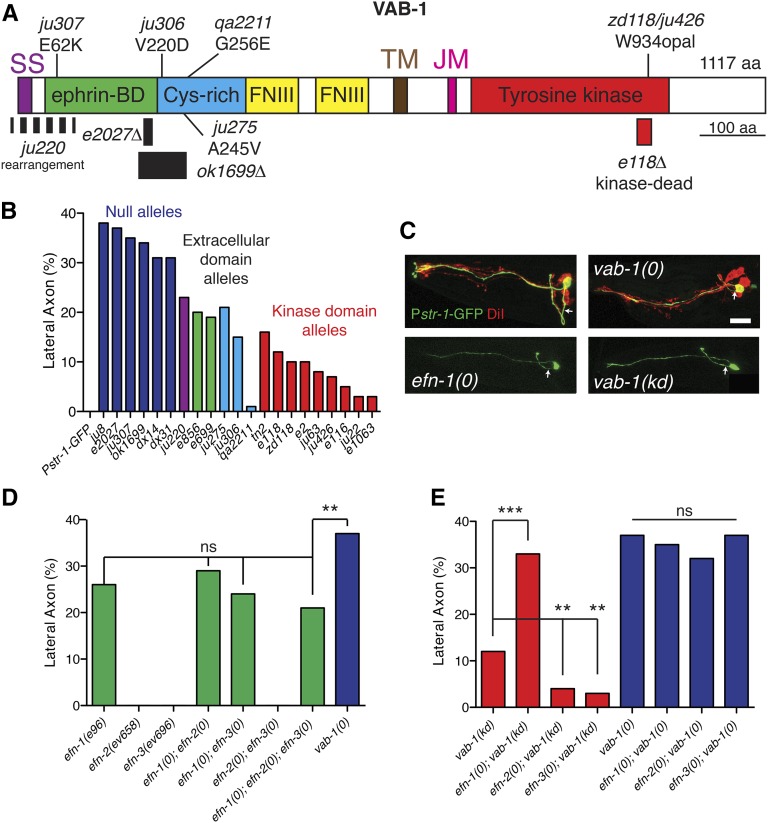
Figure 1.
Ventral guidance of amphid commissure axons is dependent on EFN-1-VAB-1 signaling. (A) Domains of VAB-1 and locations of molecular lesions. Previously isolated deletion alleles e2027(null) and e118(kd) are included for reference. ok1699 is a deletion and ju220 is a rearrangement of unknown structure. SS, signal sequence; TM, transmembrane domain; JM, juxtamembrane domain. (B) Quantitation of AWB guidance defects in Eph receptor null mutants (ju307, ju8, e2027, ok1699, dx14, and dx31), extracellular domain alleles (ju220, ju275, e856, e699, and ju306), and kinase dead alleles (tn2, e118, zd118, e2, ju63, e116, ju22, and e1063). Color coding corresponds to region of protein affected by mutation. (C) Amphid axon guidance in vab-1 and efn-1 mutants; AWB (Pstr-1-GFP, green) and DiI staining (red). Confocal projections, anterior is left and dorsal is up. Arrows indicate axon extending from cell body. Bar, 10 μm. (D) Quantitation of AWB guidance defects in efn mutants and double mutants. Asterisks indicate compound mutants significantly different from the efn-1 single mutant. (E) Quantitation of guidance defects in double mutants between each ligand and the vab-1(e118) kinase dead receptor strain or double mutants between each ligand and the receptor null vab-1(e2027). N > 50 neurons per genotype in this and all subsequent bar charts, except where N is indicated in the bar. Statistics, Fisher exact test: *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.