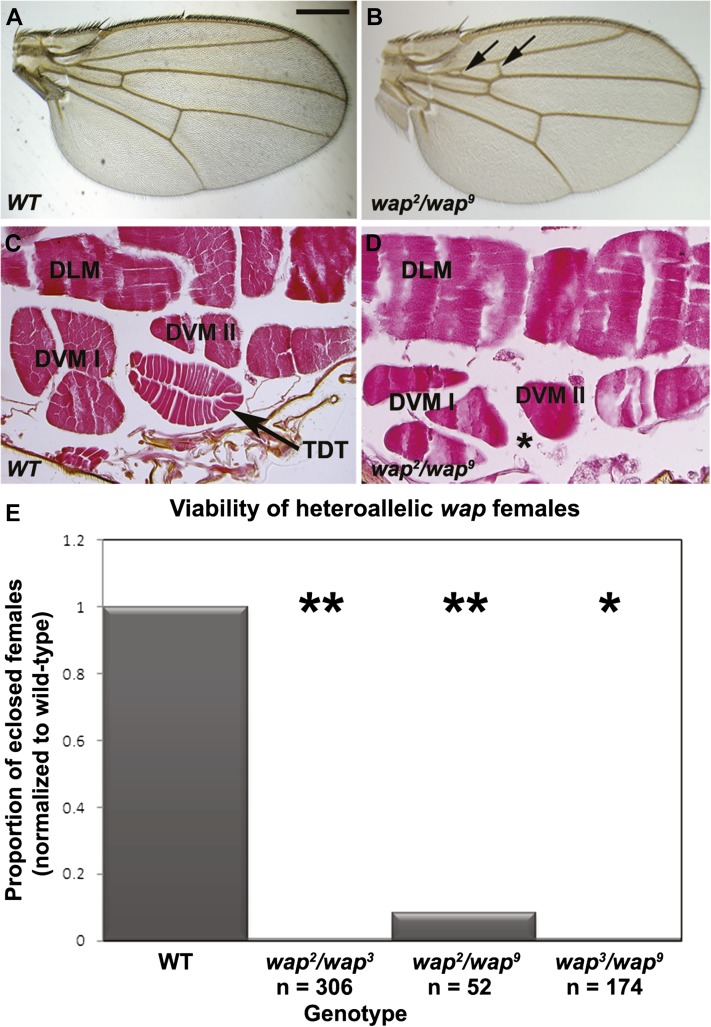
Figure 1.
wap mutants show three phenotypes. (A and B) In the wings, whereas wild-type (WT) wings have two crossveins (A), a proportion of wap mutants show additional crossveins between L2 and L3 (B, arrows). (C and D) In horizontal sections of the adult throrax, wild type shows a prominent tubular jump muscle, the TDT muscle (C, arrow); by contrast, wap mutants do not have a detectable jump muscle (D, asterisk). DLM, dorsal longitudinal indirect flight muscle; DVM, dorsoventral indirect flight muscle. (E) Compared to control female siblings, whose viability is normalized to 1.0, wap heteroallelic combinations show extremely low viability. n represents the total number of females scored from a cross of FM7/wapx females crossed to wapy/Dp(1;Y)y+mal171 males, in which 50% of the female progeny would be expected to be of the heteroallelic genotype. Bar, 400 µm for A and B; 50 µm for C and D.