Figure 2.
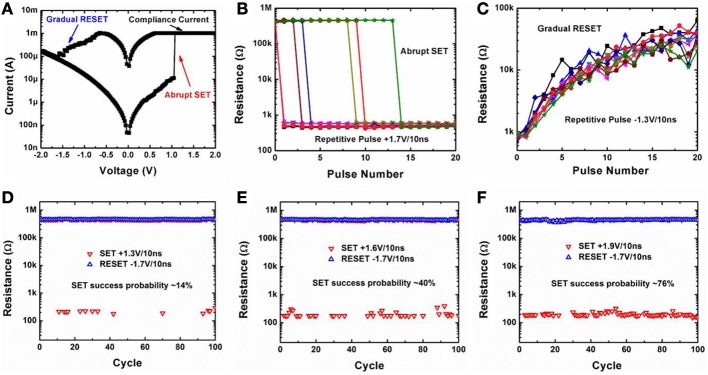
(A) Measured DC I-V switching characteristics of the oxide synaptic device. Abrupt SET transition and gradual RESET transition is observed. (B) Measured abrupt SET transition starting from the off-state (~500 kΩ) by repetitive SET pulses (+1.7 V/10 ns), in which case the device functions as a binary synapse. (C) Measured gradual RESET transition starting from the on-state (~500 Ω) by repetitive RESET pulses (−1.3 V/10 ns), in which case the device functions as an analog synapse. Results from 10 independent testing runs are shown. (D–F) Measured SET/RESET continuous cycling with different SET pulse amplitudes +1.3 V/10 ns, +1.6 V/10 ns, +1.9 V/ 10 ns, respectively. With the increase of SET pulse amplitude, the SET success probability increases as well. The SET transition becomes stochastic under weak programming condition, thus a stochastic learning rule can be utilized in such binary synapse. All the data in this figure were obtained from a single device that is representative of the devices measured.
