Figure 4.
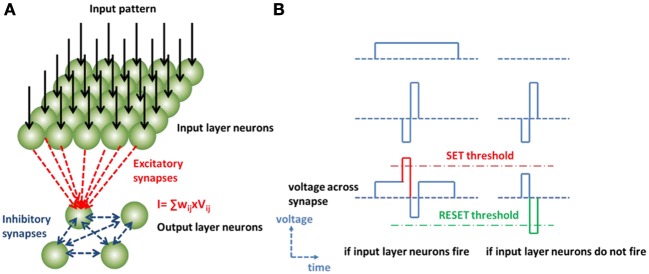
(A) Neuromorphic system based on winner-take-all neural network. In the system-level simulation, 32 × 32 neurons in the input layer are connected with 2 × 2 neurons in the output layer through 4096 oxide based excitatory synaptic devices. Every neuron in the output layer also connects to one another through inhibitory synapses based on fixed resistors. (B) The spiking scheme for binary synapse with stochastic learning: the pre-synaptic forward spike from the input layer neuron is designed to be a long but small positive pulse (e.g., +0.8 V/500 ns), the post-synaptic backward spike is designed to be a short two-phase pulse with a small negative pulse (e.g., −0.8 V/10 ns) followed by a large positive pulse (e.g., +1.9 V/10 ns). If both the input layer neuron and the output layer neuron fire, the synapse faces an actual SET programming pulse (e.g., +1.6 V/10 ns); if only the output layer neuron fires, the synapse faces an actual RESET programming pulse (e.g., −1.9 V/10 ns). Thus, the synapse conductance map between the input layer and the output layer tends to mimic the input pattern light intensity.
