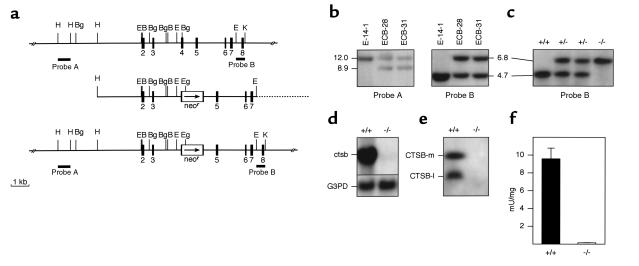
Figure 1.
Targeted disruption of the ctsb gene. (a) Strategy for inactivation of the ctsb-gene by homologous recombination in embryonic stem cells. (Top) Genomic structure and partial restriction map of the wild-type ctsb-locus (15, 47, 48). Exons are numbered and indicated by black boxes. External probes A and B used for Southern blot analyses are represented by black bars. (Middle) Targeting construct pMCB-11/1neo with 7.7 kb homology to the ctsb gene locus. A neomycin-resistance cassette was inserted into a BglII site in exon 4. The arrow marks the direction of transcription of the neomycin gene. (Bottom) Predicted ctsb-locus after homologous recombination. Broken line: plasmid vector pBluescriptII SK (+). B, BamHI; Bg, BglII; E, EcoRV; Eg, EagI; H, HindIII; K, KpnI. (b) Southern blot analysis of targeted ES cell clones. The 3′-external probe B was hybridized to BglII digested genomic DNA from wild-type E-14-1 ES cells and ES cell clones ECB-28 and ECB-31 with a targeted ctsb allele as indicated by the presence of an additional 6.8-kb DNA fragment. The 5′-external probe A was hybridized to KpnI and EagI digested DNA from the same ES cell clones, confirming homologous recombination in clones ECB-28 and ECB-31. (c) Southern blot analysis of tail DNA from offspring of an intercross of ctsb heterozygotes. Genotypes of progeny are indicated. (d) Northern blot analysis of ctsb mRNA expression. Total RNA was hybridized to a partial ctsb cDNA and a murine glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase probe (G3PD). (e) Western blot analysis of CTSB protein expression from kidney lysosomal extracts; CTSB-m: mature CTSB (single chain form); CTSB-l: large subunit (two chain form). (f) CTSB enzyme activity in liver lysosomal fractions expressed as mU/mg protein (± SD; n = 3).