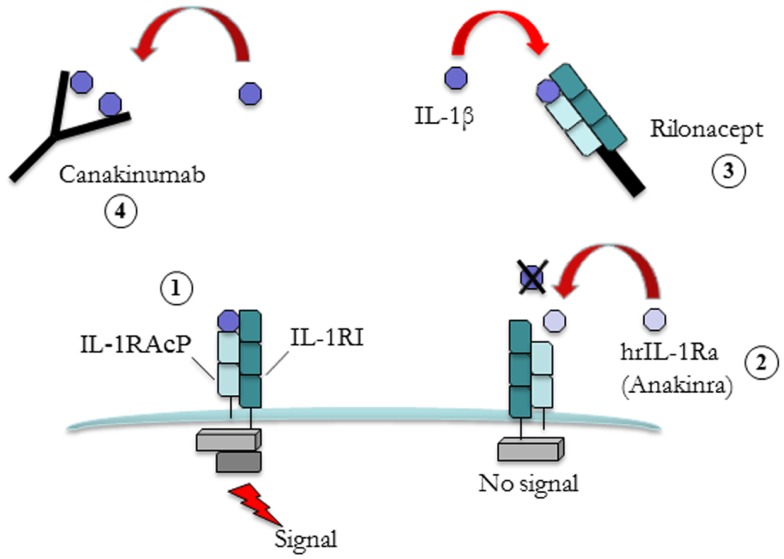
Figure 1.
Different strategies for IL-1 blockade. Free interleukin (IL)-1b binds to type 1 IL-1 receptor (IL-1R1) and to the adaptor protein IL-1RAcP leads to signal transduction (1). Human recombinant IL-1 receptor antagonist (hrIL-1Ra, Anakinra) (2) competes with free IL-1β for the binding with IL-1R1 but not with the adaptor protein, thus preventing signal transduction. Rilonacept (3) is a fusion protein comprising the extracellular domains of the IL-1β receptor (IL-1RI) and adaptor protein (IL-1RAcP) attached to a human IgG molecule. Its action is to bind to circulating IL-1β. The same mechanism of action is also valid for Canakinumab (4), a fully humanized anti-IL-1 monoclonal antibody.