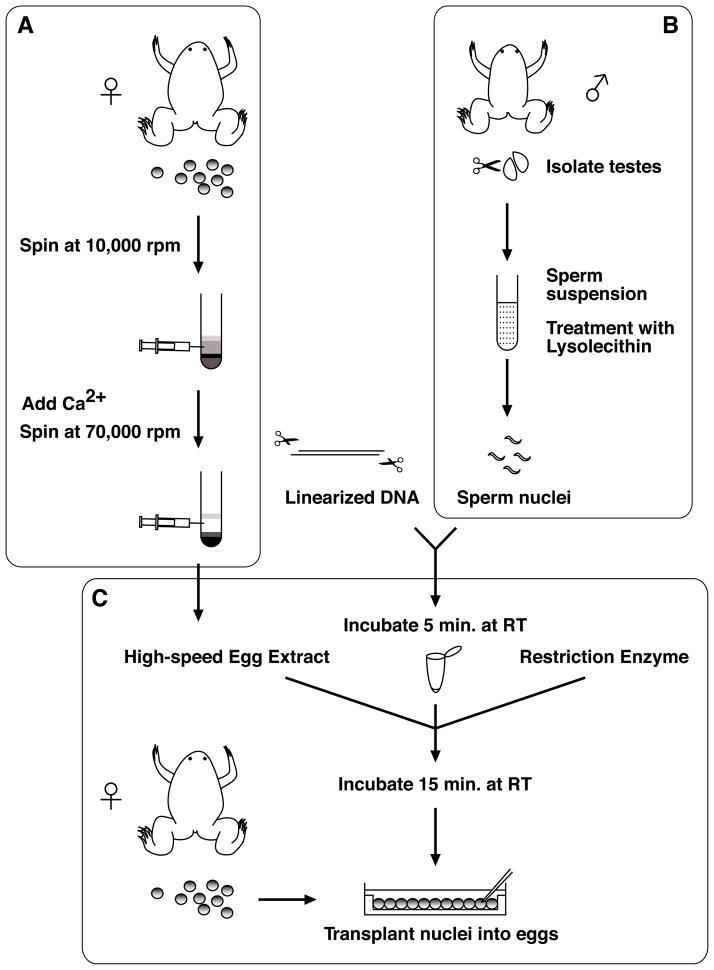
Fig. 1.
Transgenesis procedure includes: (A) Preparation of egg extracts; (B) Sperm nuclei preparation; and (C) Nuclear transplantation. The egg extracts and sperm nuclei can be stored at −80°C. (A) Calcium is added to allow the crude egg extract (which are held in meiotic arrest) to progress to interphase, and a high-speed centrifugation is performed to obtain the cytosolic fraction. (B) Testes are macerated and filtered, and then the sperm suspension is treated with lysolecithin to disrupt the plasma membrane of the cells. (C) Sperm nuclei are incubated with linearized DNA for a brief period of time. High-speed egg extracts and a restriction enzyme are added. The egg extracts partially decondenses chromosomes and the restriction enzyme stimulates recombination by creating double-strand breaks, facilitating integration of DNA into the genome. Diluted nuclei are transplanted into unfertilized egg.