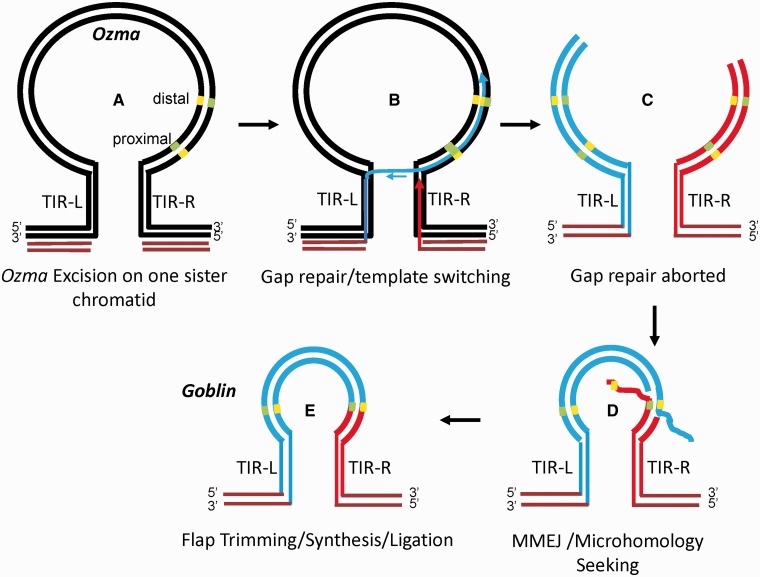
Fig. 7.—
Hypothetical model for the formation of Goblin. The microhomologous sites at the break points are located in the 3′ subterminal region of Ozma element. Yellow and green short bars, complementary microhomologous sites. Ozma is drawn as a loop structure for convenient illustration of template switching. (A) Double-stranded break formed after the excision of Ozma on one of the two sister chromatids. (B) Gap repair initiated and template switching occurred after the replication of the left TIR. When the 3′-end of the top strand of the left TIR is synthesized, it invades the DNA sequences on the right TIR for replication. (C) Gap repair aborted and the newly synthesized strands are released from the template and the lagging strands synthesized. Microhomologous sites on the newly synthesized DNA are in direct repeat orientation of that on the sequences close to the right TIR. (D) Resection occurs to expose the microhomologous sites that anneal to each other, forming single-stranded flaps with the unannealed strands. (E) Flap trimming, synthesis, and ligation, the newly synthesized double-stranded DNA joins the sequences on the right end between the left distal and the right proximal microhomologous sites. Maroon lines, the sequences flanking the excised Ozma; black lines, unexcised Ozma with flanking sequences; blue lines, newly synthesized DNA from the left; red lines, newly synthesized DNA from the right.