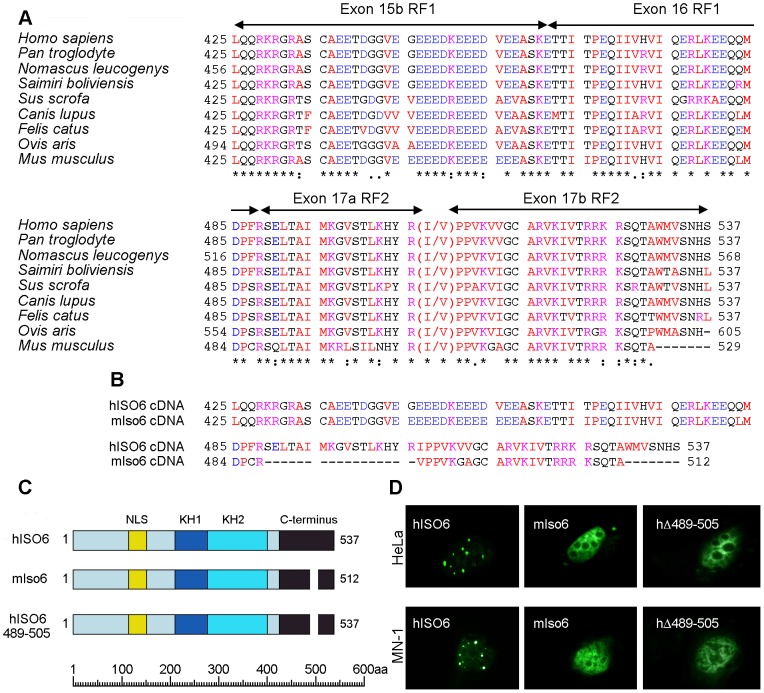
Figure 5. The Cajal body localization signal of human ISO6 is localized to a 17aa C-terminal domain.
(A) Evolutionary conserved C-termini of FMRP ISO6. ClustalW multiple sequence alignment of predicted FMRP ISO6 isoforms from different organisms compared to the experimentally determined human ISO6 sequence. Exon positions and numbering are indicated (see Figure S4). GenBank accession numbers : Sus scrofa ref|XP_003360519.1|; Felis catus ref|XP_004000999.1|; Ovis aries ref|XP_004022340.1|; Saimiri boliviensis boliviensis ref|XP_003939137.1|; Canis lupus familiaris ref|XP_003435591.1|; Nomascus leucogenys ref|XP_003271865.1|; Homo sapiens ref|NP_001172004.1| and [17]; Pan troglodytes ref|XP_003317790.1|; Mus Musculus (this study). (B) C-terminal amino acid sequences of hISO6 [17] and a mouse ISO6 variant [35] determined from cloned cDNAs. (C) Schematic representation of GFP hybrids of full-length human ISO6 and the shorter murine ISO6 variant (mIso6) and the GFP-human ISO6 with the 17aa deletion and their localization (D) in human HeLa and murine MN-1 cells after transient transfection.