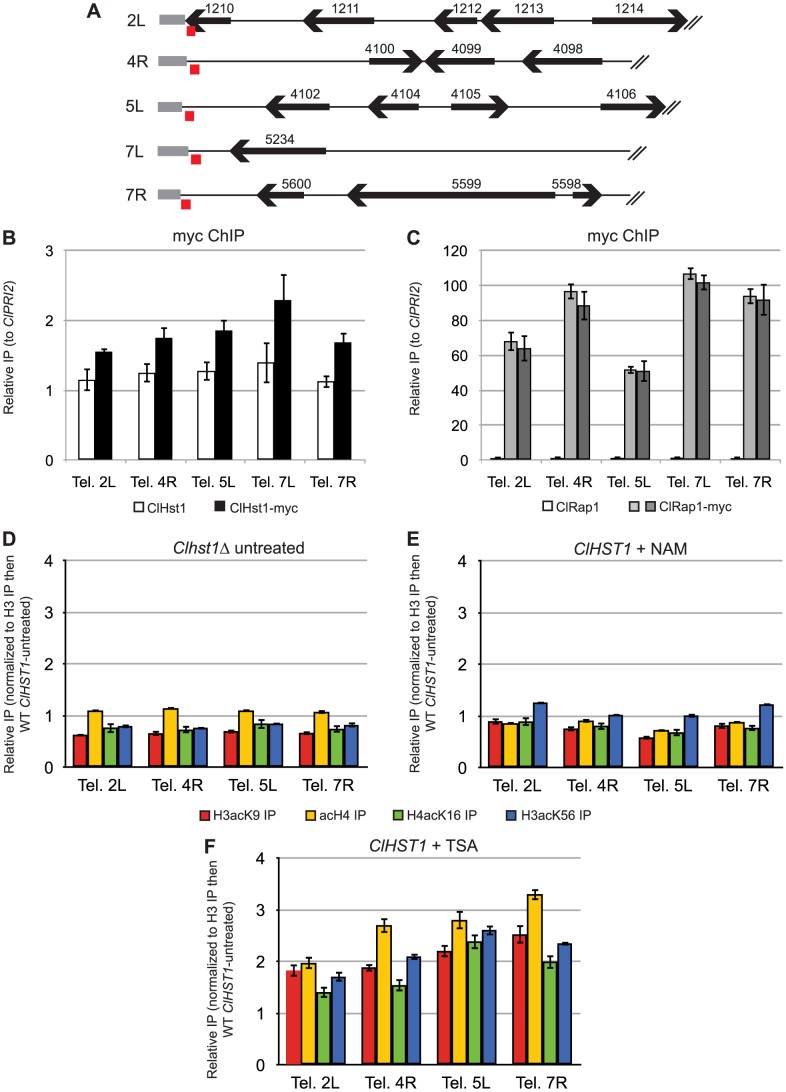
Figure 5. ClHst1 is not associated with telomeres.
(A) Diagrams represent the genetic features of 10 kbp at ends of contigs bearing telomere repeat sequences. The positions of genes (black arrows), telomere repeat sequences (gray boxes), and PCR products used for chromatin IP analysis (red boxes) are shown. Two dubious ORFs have been omitted. CLUG_04101 overlaps the telomere repeat sequence of contig 5L, and CLUG_04103 is antisense to CLUG_4102. (B) The association of ClHst1 with telomeres was examined by chromatin IP. Anti-myc antibody was used to immunoprecipitate proteins from ClHST1 (LRY2826) or ClHST1-MYC (LRY2858) yeast. The relative enrichment of each probe compared to the control locus, ClPRI2, is indicated. (C) The association of ClRap1 with telomeres was examined by chromatin IP. Anti-myc antibody was used to immunoprecipitate proteins from ClRAP1 (LRY2826) or ClRAP1-MYC (LRY2859, LRY2860) yeast. The relative enrichment of each probe compared to the control locus, ClPRI2, is indicated. (D–F) The change in acetylation of histones H3 and H4 at the telomeres was examined in deacetylase-deficient yeast relative to wild-type. Tetra-acetylated H4, H4-K16Ac, H3-K9Ac, or H3-K56Ac was immunoprecipitated from yeast. For each immunoprecipitation, the enrichment was determined relative to that of total H3, and this value was compared to the value for wild-type untreated cells. Yeast strains used were (D) Clhst1Δ (LRY2671), (E) ClHST1 (LRY2544) treated with 25 mM nicotinamide (NAM), or (F) ClHST1 (LRY2544) treated with 10 µM trichostatin A (TSA).