Figure 3.
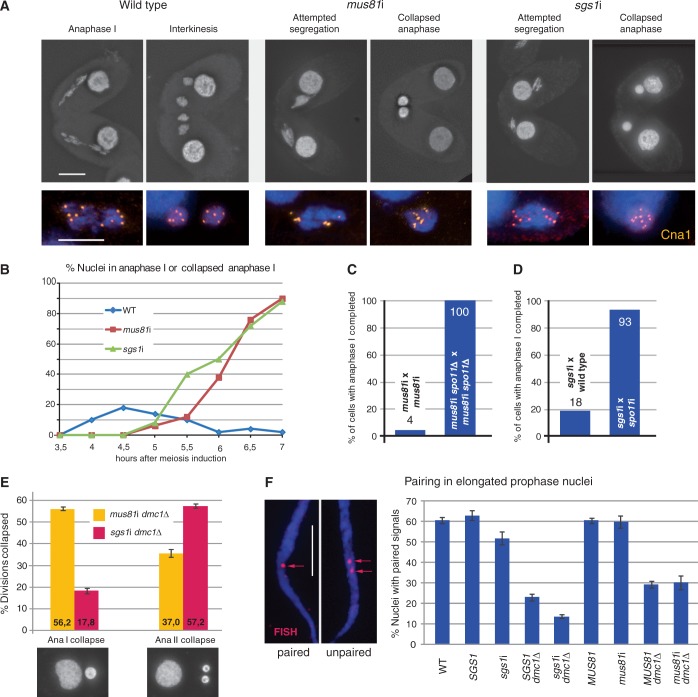
Depletion of Mus81 and Sgs1 causes DSB-dependent meiotic segregation defects. (A) In the WT, homologous chromosomes separate in anaphase I and form two distinct chromatin masses in telophase I–interkinesis. In mus81i and sgs1i meiosis, chromosomes collapse back into a single diploid nucleus after an attempted anaphase I. Staining of the centromere marker Cna1 (orange) shows the orientation of five centromeres to each of the opposite poles and five centromeres in each daughter nucleus after complete separation of the homologs in the WT. In the mutants, collapsed nuclei contain 10 centromeres. (B) Quantification of the segregation defect. WT meiotic nuclei pass through anaphase I, whereas mutants arrest with collapsed anaphase I nuclei. Hundred cells were evaluated for each genotype and timepoint. (C) Spo11 depletion rescues the mus81i segregation defect. mus81i strains were depleted of Spo11 by SPO11 knockout. All mus81i spo11Δ cells completed anaphase I 5.5 h after induction of meiosis (n = 50 cells for each phenotype). (D) Spo11 depletion rescues the sgs1i segregation defect. sgs1i cells were depleted of Spo11 by spo11 RNAi of their mating partner. spo11 RNAi is transferable, i.e. if one of the mating partners expresses interfering RNA, both cells display the depletion phenotype. spo11 RNAi efficiency was monitored by the failure of micronuclei to elongate during meiotic prophase (see main text). The sgs1i phenotype is limited to the cell expressing siRNA and is attenuated by mating to a non-sgs1i partner. Therefore, the frequency of successful anaphases was scored in the partner affected by spo11 sgs1 double RNAi and compared with sgs1i × WT pairs. n = 100 cells for each genotype. (E) dmc1Δ mus81i and dmc1Δ sgs1i double mutants are partially rescued from the anaphase I defect and undergo defective anaphase II. Shown for each genotype are the mean values ± S.D. from three experiments with 100 nuclei counted in each. An unaccounted-for percentage of cells contained three or four nuclei, where one or both products of a first division may have undergone a second division or where nonseparating bivalents or chromosomes had formed extra nuclei. (F) Pairing in the elongated prophase nucleus. Examples of paired (FISH signals fused) and unpaired (FISH signals separate) homologous loci (red arrows) are shown. SGS1 and MUS81 genotypes carry the respective RNAi hp constructs, but RNAi was not induced; hence, they resemble the WT control. In the absence of Sgs1 but not of Mus81, homologous pairing is reduced both in the WT and in the dmc1Δ background, in which recombination takes place primarily between sisters (30). Values are means of three repeats with 100 nuclei evaluated, each. Error bars indicate standard deviation. Bars in A and F: 10 µm.