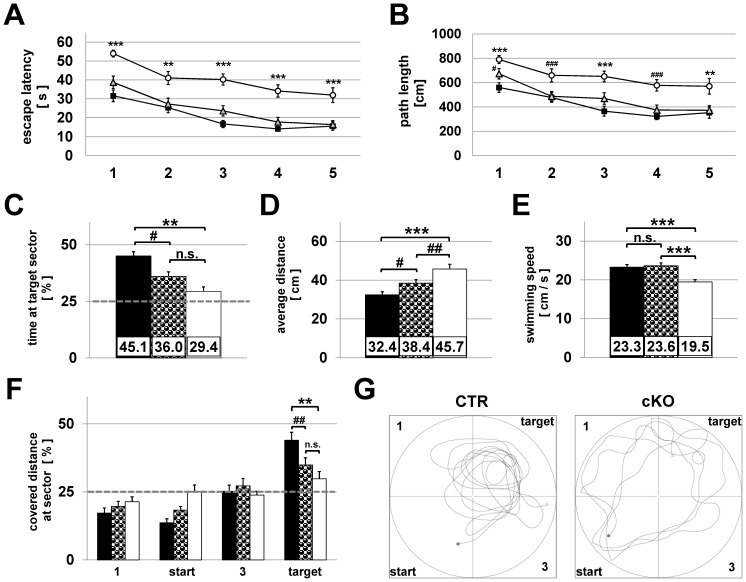
Figure 7. Morris Water Maze task.
cKO mice show a significantly impaired space learning and spatial memory compared to HET and CTR animals. (A) & (B) During the first five days place-learning was analysed by assessing (A) the time and (B) the path-length to reach the hidden platform. Data of the acquisition trials were averaged across four trials per day. Data points are mean ± SEM (cKO: white circles, n = 18; HET: grey triangles, n = 19 and CTR: black squares, n = 20). (C) to (F) During Morris Water Maze retention trials, the platform was removed from the basin and spatial memory was analysed by assessing the mousés ability to recall the position of the formerly hidden platform. Means + SEM are shown. (C) Percentage of total time spent at the target sector for CTR (black, n = 20), HET (half tone, n = 19) and cKO mice (white, n = 18). (D) Average distance to platform position during retention trial. (E) Average swimming speed of mice during retention trial. (F) Percentage of distance covered at the four water maze sectors. Chance level is indicated by the dashed line. # P<0.05; ## P<0.03; ** P<0.003; *** P<0.001 (one-way ANOVA & Student-Newman-Keuls post hoc test). (G) Illustration of two representative swimming tracks of a CTR (left) and cKO animal (right) during the retention trial at day 6 of the Morris Water Maze experiment. Circles at the target sectors indicate the position of the platform during acquisition trials.