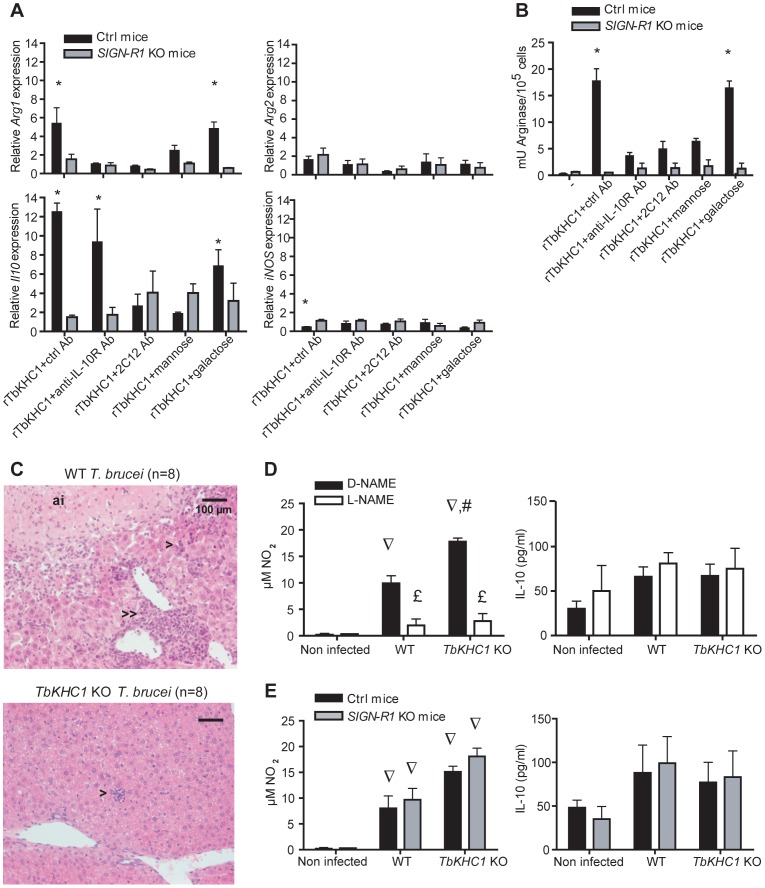
Figure 6. SIGN-R1 receptor contribution to myeloid cell activation and liver injury.
(A,B) Effects of rTbKHC1 on myeloid cells from non-infected control (Ctrl) or SIGN-R1 KO mice (A: relative expression of Arg1, Arg2, Il10 and iNOS genes; B: arginase activity in presence of indicated antibodies or sugars). Data are means ± SEM of 3 individual mice of one representative from 3 independent experiments. * p<0.05 compared to non-stimulated (-) cells. (C) Effects of rTbKHC1 on liver injury: microscopic analysis (hematoxylin-eosin staining, magnification 20×) of sections from WT- and TbKHC1 KO-infected mice at day 30 p.i. Anoxic infarcts (ai), periportal (>>) and lobular (>) mononuclear cell infiltrates were representative of 8 animals tested in 2 independent experiments. (D) Spontaneous NO and IL-10 secretions in spleen myeloid cell supernatants from WT- and TbKHC1 KO-infected mice treated with D-NAME or L-NAME (day 30 p.i.). (E) Idem as D in SIGN-R1 KO and control (Ctrl) mice. Data are means ± SEM of 3–4 individual mice of one representative from 3 independent experiments. ∇ p<0.05 comparing WT or TbKHC1 KO- infected mice to non-infected mice; £ p<0.05 comparing L-NAME and D-NAME treatment in WT- or TbKHC1 KO-infected mice; # p<0.05 comparing WT- and TbKHC1 KO-infected mice.