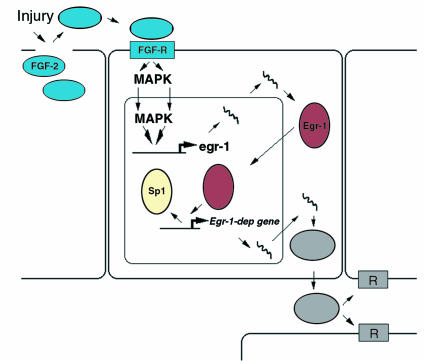
Figure 1.
Model of Egr-1–dependent response to injury. Injury to vascular cells releases preformed endogenous growth factors (such as FGF-2), which activate Egr-1 gene expression in a paracrine manner via mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs). Egr-1 protein can, in certain promoters, displace Sp1 from overlapping binding sites and increase the expression of pathophysiologically relevant genes whose products contribute to neointima formation. Rec, receptor.