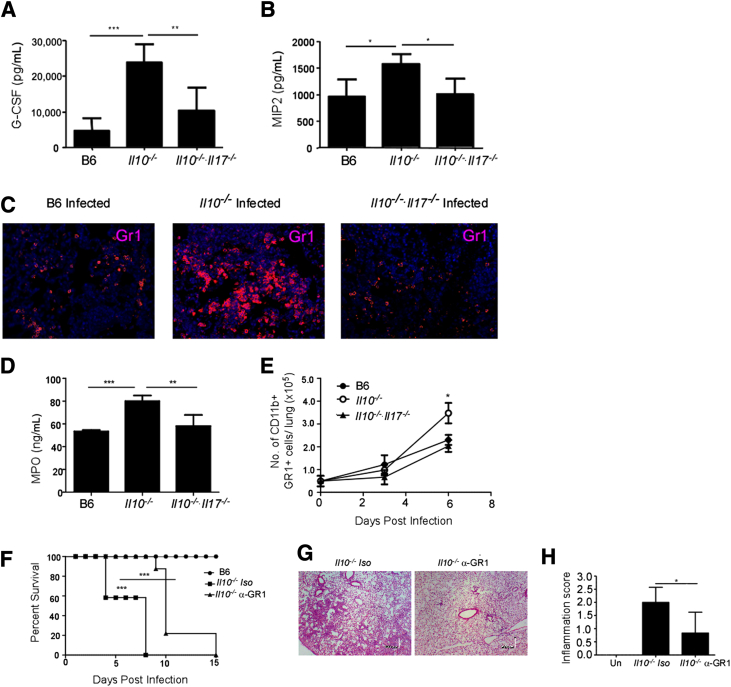
Figure 3.
A and B: Neutrophils contribute to lung pathological characteristics and increased mortality in Il10−/− mice after F. tularensis LVS infection. B6, Il10−/−, and Il10−/−/Il17−/− mice were infected with 1000 CFUs F. tularensis LVS intratracheally, and on day 6, lung homogenates from infected B6 and gene-deficient mice were assayed for G-CSF (A) and MIP-2 (B) protein levels. C: Serial sections of day 6–infected, formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) lungs were stained with antibodies specific to GR1. D and E: The level of MPO activity was determined in lung homogenates (D), and neutrophil accumulation (CD11b+ GR1+ cells) in the lungs was enumerated using flow cytometry (E). The data points represent the means ± SD of values from 6 to 10 mice. F: Il10−/− mice were infected with 1000 CFUs F. tularensis LVS intratracheally and treated with Gr1-depleting antibody or isotype control and monitored for survival. G and H: Statistical significance was by log-rank test for the survival studies. Day 6, formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) serial lung sections were stained with H&E (G), and sections were scored for percentage of inflammation, as described in Materials and Methods (H). The data points represent the means ± SD of values from 6 to 10 mice. ∗P ≤ 0.05, ∗∗P ≤ 0.005, and ∗∗∗P ≤ 0.0005. One experiment is representative of two or more.