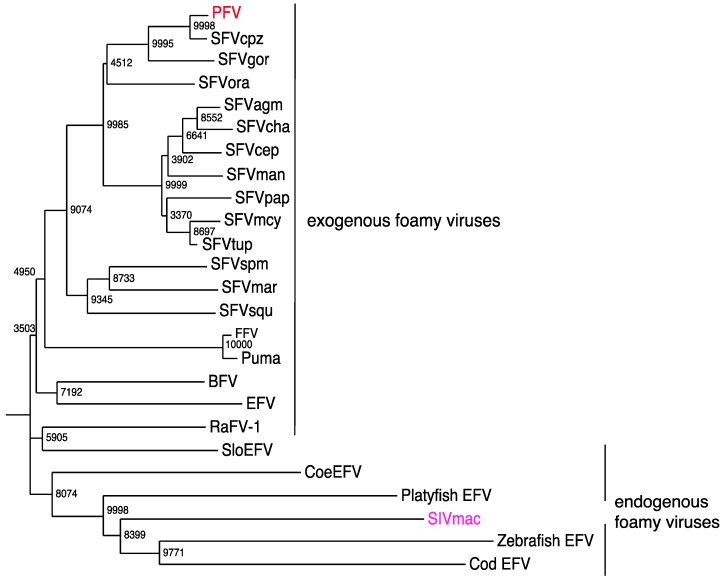
Figure 4.
Phylogeny of current endogenous and exogenous FV pol amino acid sequences (from the active center-specifying integrase sequences and comprising 142 codons). A neighbor-joining tree was calculated by using the Maximum Composite Likelihood method with a bootstrap test of 10,000 replicates. BFV, bovine FV (NP_044929.1); EFV equine FV (NP_054716.1); PFV, prototypic FV (in red) (Y07725.1); SFVcpz, SFV from chimpanzee (CCP47057); SFVgor, SFV from gorilla (AY195688.1); SFVora, SFV from orangutan (CAD67562); SFVagm, African green monkey (Cercopithecus aethiops) FV (YP_001956722.2); SFVcha, SFV from Chlorocebus aethiops (CAM34599); SFVcep, SFV from Cercopithecus pygerythrus (AAV92627); SFVman, SFV from mandrill (ADO65890.1); SFVpap, SFV from Papio (CAM34655); SFVmcy (previously SFVmac) from Macaca mulatta, SFV from Macaca cyclopis (CAA41394.1); SFVtup, SFV from Tupaia [155] (AGN49359); SFVspm, SFV from spider monkey (ABV59399.1); SFVmar, SFV from marmosets (ADE06000.1); SFVsqu, SFV from squirrel monkeys (ADE05995.1); FFV, feline FV (NP_056914); Puma, FV from Puma concolor (AGC11913); RaFV-1, FV from the bat Rhinolophus affinis (AFK85015); SloEFV, endogenous FV from sloths (Katzourakis et al., 2009); CoeEFV, endogenous FV in the coelacanth (Latimeria) genome (JX006241.1); platyfish EFV, endogenous FV from platyfish (M. Schartl, personal communication); zebrafish EFV, zebrafish (M. Schartl, personal communication); and Cod EFV, codfish (M. Schartl, personal communication) genomes; integrase encoding sequences of the macaque simian immunodeficiency virus (SIVmac in magenta) (AAC57420.1) served as the outlier; the endogenous FV sequence from aye-aye (PSFVaye) [156] was not incorporated, because integrase sequences are not available.