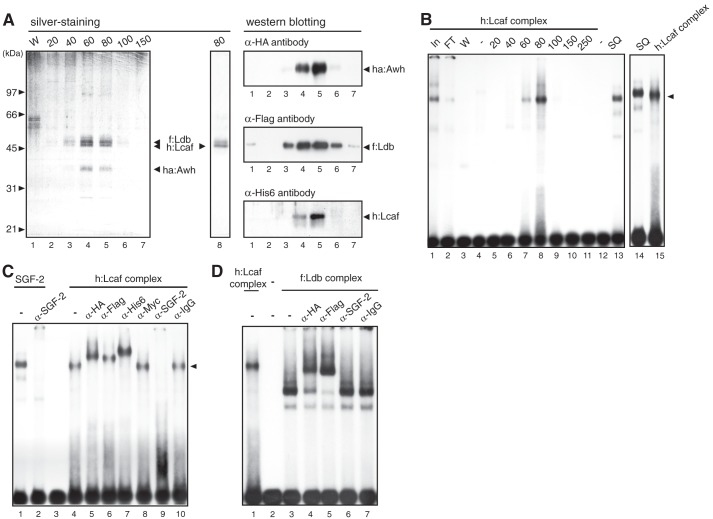
FIGURE 4.
Lcaf forms a DNA-binding protein complex with Awh and Ldb. A, left, silver-stained SDS-PAGE gel of Ni-NTA-agarose purification fractions from the extract of Sf9 cells co-expressed with ha:Awh, f:Ldb, and h:Lcaf by the baculovirus expression system. W in lane 1: wash fraction of Ni-NTA-agarose. Numbers at the top indicate imidazole concentration (in mm) for elution. Lane 8, the purified fraction from Sf9 cell extract expressing only h:Lcaf. The character of native Ldb protein with light-brown color in the silver-stained gel was also observed for recombinant Ldb protein, but the slightly slower migrating band than the h:Lcaf band in lane 8 was gray-colored, not light brown; therefore it seemed not to be Ldb. Right, Western blot analysis using Ni-NTA-agarose purification fractions. Each lane corresponds to that of the silver-stained SDS-PAGE gel shown on the left. B, EMSA using Ni-NTA-agarose fractions of h:Lcaf complex with the E box DNA probe. Numbers and SQ at the top indicate imidazole concentration (in mm) for elution and partial purified native SGF-2 fraction after Source 30Q column, respectively. Lanes In and FT indicate the extracts (In) and flow-through (FT) fraction of Ni-NTA-agarose purification, respectively. C, EMSA of h:Lcaf complex with antibodies. The h:Lcaf complex eluted by 80 mm imidazole was used with each antibody indicated at the top. Anti-IgG and anti-c-Myc antibodies were used as negative controls. D, EMSA of f:Ldb complex with antibodies. The f:Ldb complex eluted by 80 mm imidazole was used with each antibody indicated at the top.