FIGURE 1.
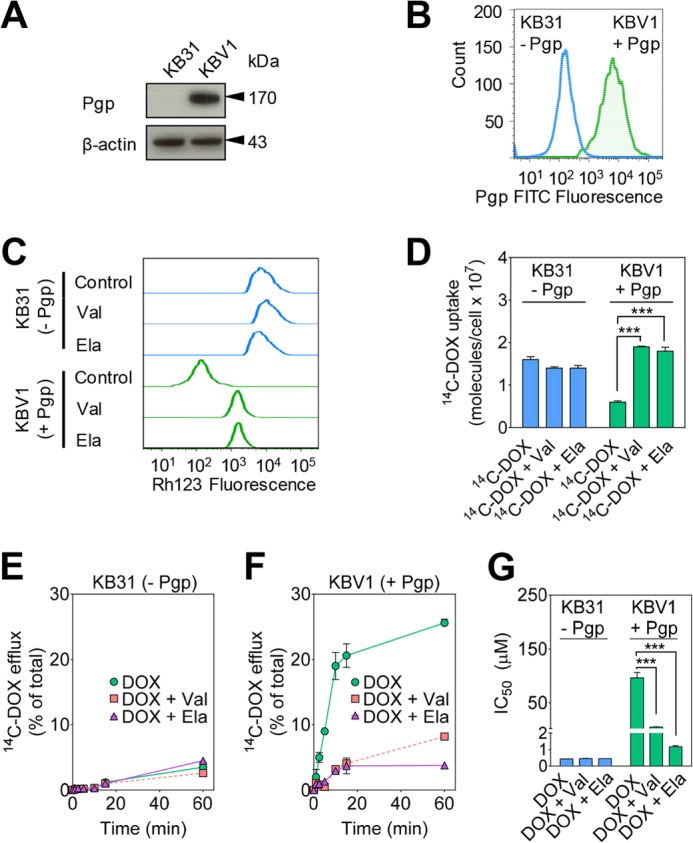
Functional Pgp causes DOX resistance. A, Western blot analysis showing that Pgp is only expressed in KBV1 (+Pgp) and not in KB31 (−Pgp) cells. β-Actin was used as a loading control. B, flow cytometry demonstrates higher plasma membrane expression of Pgp in KBV1 (+Pgp) cells than KB31 (−Pgp) cells. Cells were not permeabilized to prevent intracellular staining of Pgp prior to flow cytometric analysis. C, Rh123 accumulation is decreased in KBV1 (+Pgp) control cells compared with KB31 (−Pgp) control cells, whereas Pgp inhibition increases Rh123 accumulation only in KBV1 (+Pgp) cells. Briefly, cells were preincubated with either control medium or the Pgp inhibitors Val (1 μm) or Ela (0.1 μm) for 30 min at 37 °C. Cells were then loaded with Rh123 (1 μg/ml) for 15 min at 37 °C in the presence or absence of these inhibitors. D, Pgp inhibitors increase [14C]DOX uptake only in KBV1 (+Pgp) cells. Briefly, KBV1 (+Pgp) or KB31 (−Pgp) cells were preincubated with either control medium or the Pgp inhibitors Val (1 μm) or Ela (0.1 μm) for 30 min at 37 °C. [14C]DOX was then added, the incubation continued for 30 min at 37 °C, and then the cells were washed. E and F, Pgp inhibitors block efflux of [14C]DOX only from KBV1 (+Pgp) cells. Briefly, cells were labeled with [14C]DOX for 30 min at 37 °C, washed, and then reincubated for up to 60 min at 37 °C in the presence or absence of the Pgp inhibitors Val (1 μm) or Ela (0.1 μm). G, DOX cytotoxicity (IC50/72 h) is potentiated by the Pgp inhibitors Val (1 μm) or Ela (0.1 μm) in KBV1 (+Pgp) cells but not KB31 (−Pgp) cells. The results in A–C are representative of three experiments, whereas those in D–G are mean ± S.D. (three experiments with at least four replicates in each experiment). ***, p < 0.001 versus control.
