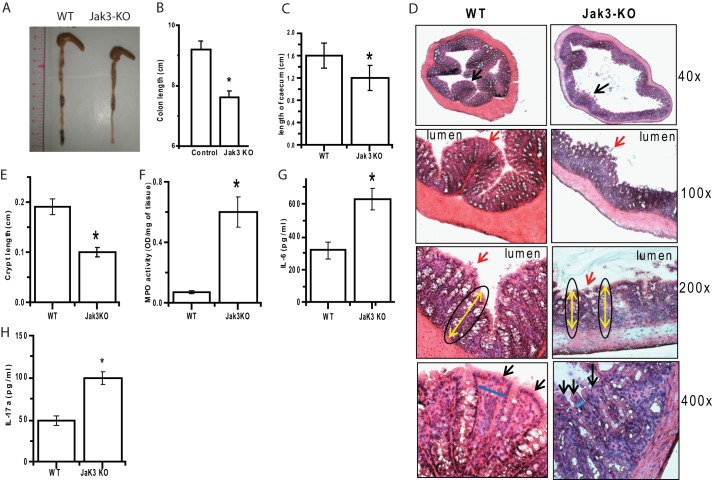
FIGURE 2.
Increased basal colonic inflammation in Jak3 KO mice. A–C, shortening of colon and cecum lengths in Jak3 KO mice. A, representative (n = 5) macroscopic images of the colons with cecum from WT and KO mice are shown. Colon (B) and cecum (C) lengths of WT and KO mice were calculated using NIS Element software (Nikon®), and mean values (n = 5) were plotted for each group. D, histological analysis of colon sections from mice treated with water. Fresh frozen colonic sections from WT and KO mice were stained with H&E; D, representative sections are shown with the indicated magnifications from each group (n = 6). Black arrows (×40) show comparison of colonic mucosa indicating perturbed epithelial architecture with interruptions in epithelial lining in KO mice. Red arrows (×100 and ×200) indicate discontinuous mucous layer overlaying epithelial mucosa. Yellow double arrows (×200) with oval lining around indicates reduced crypt lengths in KO mice. Black arrows and blue lines (×400) indicate reduced crypt width with irregular arrangement of cells from the base of the crypt to the luminal surface in KO mice. E, epidermal thickness (crypt length) from H&E-stained colonic sections (from D) of WT and KO was quantified using the NIS Element imaging software (Nikon®), and mean values from each group (n = 6 mice per group) are plotted. F, increased colonic MPO activity in untreated KO mice. MPO activities in colonic tissue lysates from untreated mice were determined, and mean values from each group (n = 6 mice per group) were plotted. G and H, increased pro-inflammatory cytokines in colon of KO mice. Cytokine level in the colonic tissue lysates from WT and KO mice were measured using a mouse MultiAnalyte cytokine assay kit (Qiagen) as per the manufacturer's protocol, and mean values from each group (n = 6 mice per group) are shown. B, C, and E–H, values are mean ± S.E. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences between WT and KO groups (p < 0.05 from at least n = 3 independent experiments).