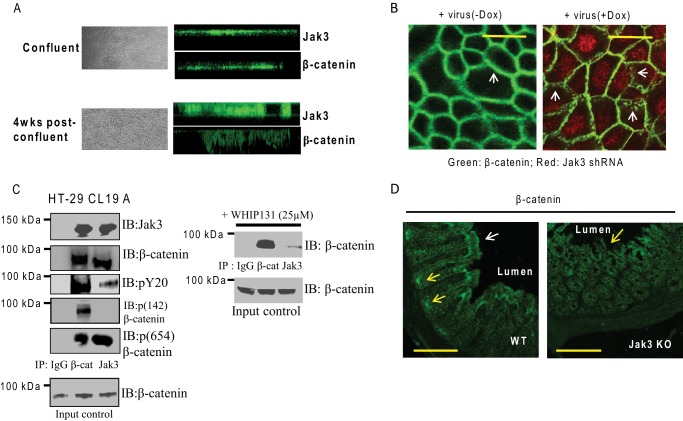
FIGURE 5.
Jak3 facilitates AJ formation through interactions with β-catenin. A, Jak3 redistributes to basolateral surfaces in differentiated human IEC. Cellular redistribution of Jak3 was determined using IFM in confluent (nondifferentiated) and 2-week post-confluent (as these had maximum expression of differentiation markers, Fig. 4A) HT-29 Cl-19a cells. Bright field images (left panels) and corresponding XZ section (right panels) of Jak3 (green)-stained cells were taken to determine the basolateral redistribution using AJ protein β-catenin as a positive control. Representative images are shown (n = 5 experiments). B, Jak3 regulates β-catenin localization to AJ. AJ localization of β-catenin was determined in 2-week post-confluent HT-29 CL-19a cells transduced with lentiviruses mentioned in Fig. 4B and grown in the presence (+Dox) or absence (−Dox) of doxycycline, and IFM was performed using antibody for β-catenin. Representative images are shown (n = 6 experiments), where the green color indicates β-catenin and the red color confirms RFP-tagged Jak3-shRNA expression-mediated knockdown of Jak3 expression (25). Note that knockdown of Jak3 expression disrupts the AJ localization of β-catenin (white arrows) as denoted by punctate green staining in Jak3-shRNA-expressing (+Dox) cells. Bar 14 μm. C, Jak3 activation facilitates its interactions with tyrosine 654-phosphorylated pool of β-catenin. Left panel, co-IP followed by IB studies were done using cell lysates from HT-29 CL-19a cells and indicated antibodies. Representative blots are shown (n = 3 experiments). C, right panel, effect of inhibition of Jak3 on the interactions between Jak3 and β-catenin was studied using co-IP followed by IB studies from lysates of HT-29 CL-19A cells treated with Jak3 inhibitor WHI-P131 (25 μm). Previously, we reported that treatment with WHI-P131 leads to inhibition of Jak3 in HT-29 CL-19A cells (12, 13, 25). D, knock-out of Jak3 affects localization of β-catenin in colonic mucosa of mice. Localization of β-catenin was studied in colonic tissue sections from WT and KO mice using IFM as described in Fig. 3A. Representative images are shown (n = 5 experiments with three tissue sections per experiment). Profuse β-catenin staining in WT colon is evident in the crypt and villus regions (yellow and white arrows, respectively), which were absent in KO mice. Scale bar, 550 μm.