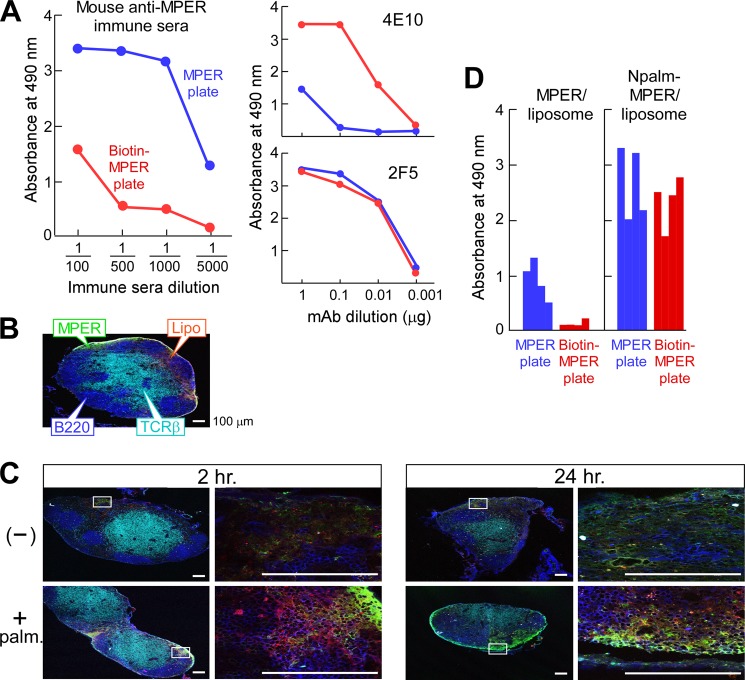
FIGURE 2.
Enhanced immunogenicity of the MPER through covalent attachment to lipid. A, serum IgG responses of a representative BALB/c mouse immunized with noncovalently attached MPER/liposome. Anti-MPER-specific IgG in the sera was determined using ELISA plates either directly coated with MPER (blue) or via biotin-MPER peptide bound to a streptavidin-coated plate (red). mAbs 4E10 and 2F5 were separately assessed as positive controls. B, localization of the palmitoylated MPER/liposome in inguinal LN 2 h post-injection. C57BL/6 mice were injected with FITC-labeled palmitoylated MPER/rhodamine-labeled liposomes. T and B cell areas were identified by anti-TCRβ (H57 mAb) (cyan) and anti-B220 (blue), respectively. C, co-localization of MPER and liposome. The association of FITC-MPER with rhodamine-liposome (top row, −) or of palmitoylated FITC-MPER with rhodamine-liposome (bottom row, + palm) in inguinal LN was monitored by confocal microscopy at 2 and 24 h after injection. Scale bars, 100 μm. D, enhanced serum IgG responses specific to MPER via immunization with palmitoylated MPER/liposome compared with free MPER/liposome. The anti-MPER specific IgG in a 1:5000 dilution of the sera from BALB/c mice (n = 4) immunized with MPER/liposome or Npalm-MPER/liposome was determined by ELISA using a MPER plate (blue) or biotin-MPER plate (red).