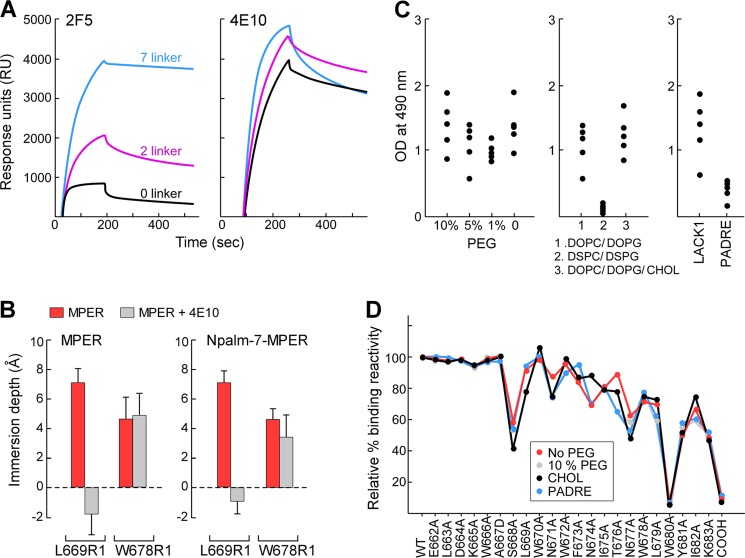
FIGURE 3.
Effect of biophysical properties of Npalm-7-MPER/liposome on immunogenicity. A, antigenicity of Npalm-MPER antigens with various linker residues. The binding reactivity of 2F5 and 4E10 was measured for Npalm-MPER peptides in DOPC/DOPG membrane by Biacore. B, comparison of membrane immersion depth values of MPER and Npalm-7-MPER peptides in the presence and absence of 4E10. Depth values between −2 to 0 Å and larger than 0 Å correspond to the lipid headgroup and acyl chain region, respectively. C, effect of PEG density (left), lipid compositions (middle), and helper peptides (right) on MPER-specific IgG responses. BALB/c mice (n = 5) were immunized three times with various MPER/liposome vaccines, and the anti-MPER-specific IgGs in a 1:5000 dilution of the sera were determined in an ELISA on biotin-MPER plate. D, immunogenicity of C variants by epitope map analysis relative to the standard liposome vaccine containing 10% PEG. The x axis labels WT and 23 variant peptides tested. The single mutation converts each residue to alanine, except the 667 mutated to aspartic acid and the C-terminal amide to carboxylate (COOH).