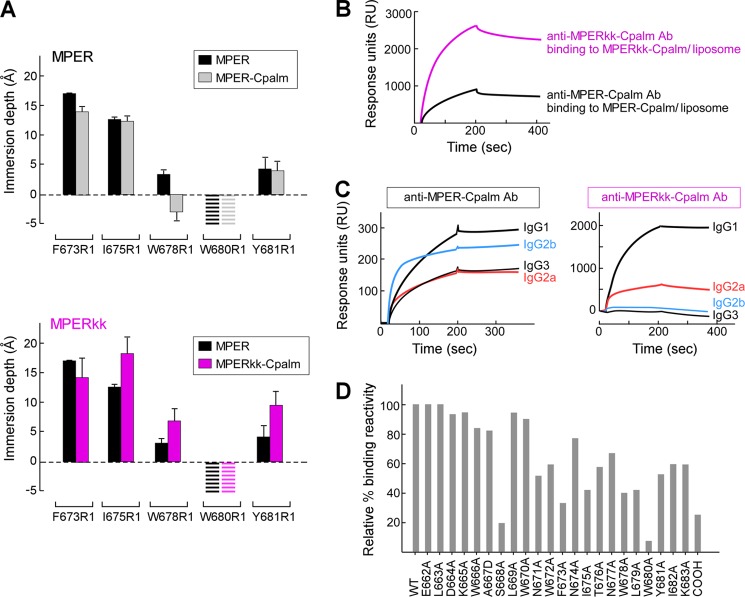
FIGURE 5.
Orientations of MPER-Cpalm versus MPERkk-Cpalm segments relative to membrane and their corresponding immunogenicity. A, EPR membrane immersion depths of MPER, MPER-Cpalm, and MPERkk-Cpalm in liposomes. The striped bars indicate complete exposure to aqueous phase (depth < −5 Å). B, binding of anti-MPER-Cpalm and anti-MPERkk-Cpalm antibodies to MPER-Cpalm or MPERkk-Cpalm/liposome (DOPC/DOPG) by Biacore. Each purified polyclonal antibody at 50 μg/ml from immune sera pooled from five immunized mice was injected over the L1 chip-bound peptide-liposome complex. C, analysis of anti-MPER-Cpalm and MPERkk-Cpalm IgG subclasses as measured by Biacore. Isotype-specific monoclonal anti-mouse IgG (10 μg/ml each) was passed over the surface of anti-MPER-Cpalm- or MPERkk-Cpalm-specific antibody bound to MPER-Cpalm/liposome or MPERkk-Cpalm/liposome arrayed on the surface of L1 chip, respectively. D, epitope mapping of anti-MPERkk-Cpalm polyclonal IgG antibody. Three independent immunizations of MPERkk-Cpalm/liposomes were carried out, with data representative of anti-MPERkk-Cpalm-specific antibody analysis from pooled serum (n = 5). The purified polyclonal IgG antibody was tested for binding affinity by Biacore.