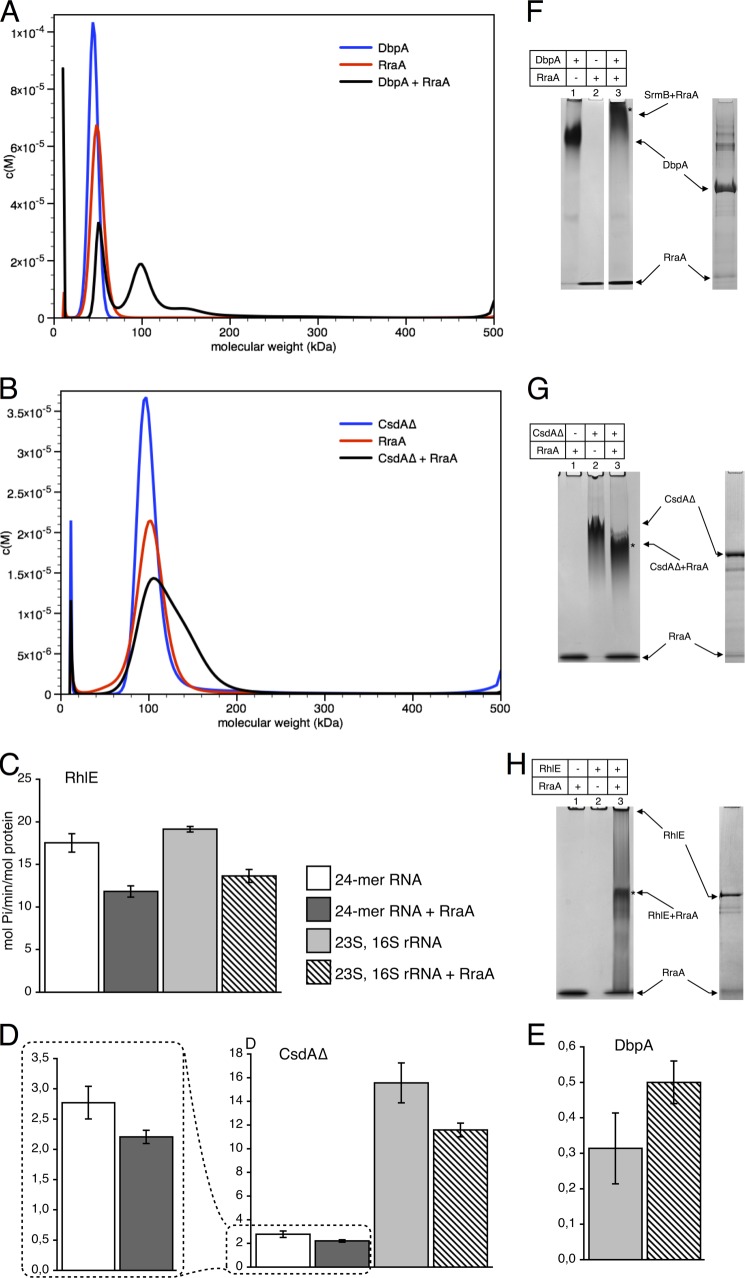
FIGURE 5.
RraA and its interactions with DbpA, CsdA, and RhlE helicases. Panels A and B show AUC analysis. The mass distribution for helicases, RraA, and the mixtures are shown in blue, red, and black, respectively. A, DbpA and RraA. B, AUC analysis of CsdAΔ, RraA, and their complex (in 300 mm NaCl). Both proteins form particles of ∼100 kDa, which corresponds to a CsdAΔ dimer and RraA hexamer. When both proteins are present a predominant peak is recorded with a shoulder of ∼150 kDa, which likely correspond to an assembly between the CsdAΔ with RraA. Panels C–E, effects of RraA on ATPase activity of the helicases. Each bar represents averaged values from at least three independent experiments, and error bars represent 2 S.D. White and dark gray bars represent reactions with 24-mer RNA substrate. Reactions with 23S and 16S rRNA are represented by light gray bars and bars filled with diagonal stripes. Bars that are dark gray or filled with diagonal stripes represent reactions with RraA. RraA was added in 3-fold molar excess (one RraA trimer per helicase molecule). In the case of CsdAΔ with 23S, 16S rRNA, and DbpA twice the amount of RraA was used (two RraA trimers per helicase molecule). Activity is expressed as mol of Pi/min/mol of protein, and the scale differs for individual helicases. Panels F–H, interactions of RraA, with the DEAD-box helicases analyzed by native PAGE. Free RhlE does not enter the gel. Bands marked with an asterisk were extracted and analyzed by SDS-PAGE to confirm the presence of both RraA and DEAD-box proteins.