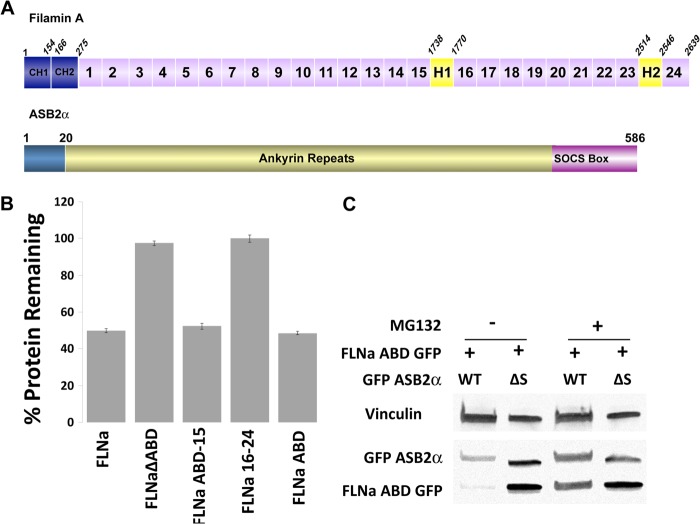
FIGURE 1.
ABD of FLNa is targeted for proteasomal degradation by ASB2α. A, schematic representation of FLNa and ASB2α. Each FLNa dimer is composed of an actin-binding domain (ABD) containing two calponin homology domains (CH1 and CH2) followed by 24 Ig-like repeats (IgFLN1–24). The repeats are interrupted by two hinge regions, H1 and H2, and mediate interaction with a majority of filamin binding partners. Filamins dimerize via IgFLN24 and form a flexible V-shaped structure. ASB2α is composed of an N-terminal region followed by 15 predicted ankyrin repeats and a C-terminal SOCS box. The SOCS box mediates interaction with a cullin family member (Cullin 5) and RING finger proteins (Rbx 1/2) by interacting with elongin BC to form an E3 ubiquitin ligase complex. B, CHO cells transiently expressing FLNa GFP, FLNaΔABD GFP, FLNaABD-15 GFP, FLNa16–24 GFP, and FLNaABD GFP were transfected with either dsRed-ASB2α or dsRed-ASB2αΔS. 48 h after transfection, cells were detached and washed with PBS, and the GFP intensity of dsRed-expressing cells was assessed by flow cytometry. Bar chart depicts mean percentage of GFP-tagged protein remaining ± S.E. in dsRed-ASB2α-expressing cells normalized to levels in dsRed-ASB2αΔS-expressing cells (see “Experimental Procedures” for details). Data are from at least seven independent experiments. C, CHO cells were co-transfected with FLNaABD GFP and GFP-ASB2α or GFP-ASB2αΔS. 30 h after transfection cells were untreated or treated with 5 μm MG132 for 18 h. 48 h after transfection, cells were lysed and immunoblotted using anti-GFP. Vinculin staining was used as a loading control.