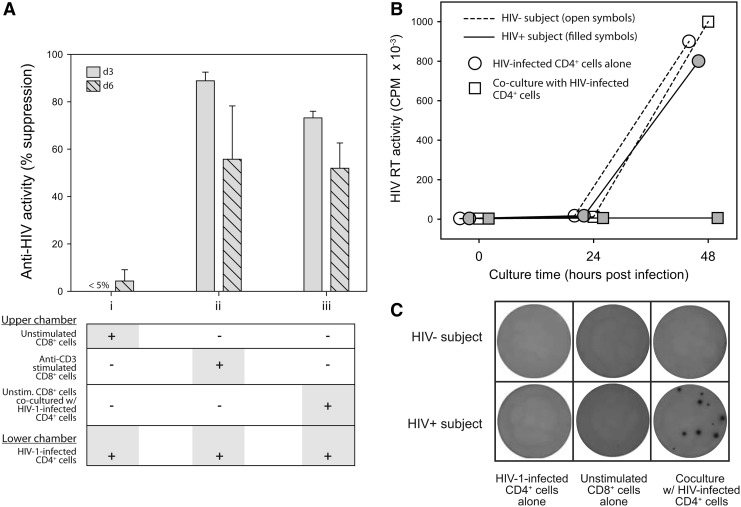
FIG. 7.
CD8+ cells suppress HIV replication in CD4+ cells by secreting IFN-α. (A) Transwell assays. Shown is the anti-HIV activity (% suppression measured at culture days 3 and 6) when (i) unstimulated CD8+ cells, (ii) anti-CD3-stimulated CD8+ cells, or (iii) unstimulated CD8+ cells and HIV-1-infected CD4+ cells were placed into the upper chamber of a transwell insert. All wells contained HIV-1-infected CD4+ cells in the lower chamber. Error bars show the standard deviations from duplicate wells, and the results shown are representative of 3 independent experiments. (B) Cell-to-cell contact assays. Shown are line-and-scatter plots of HIV replication levels, measured by RT activity, in the supernatants of CD4+ cell cultures. Acutely HIV-infected CD4+ cells were cultured alone (open symbols) or in the presence of autologous unstimulated CD8+ cells (shaded symbols) at 1:1 cell input ratios. Representative results are shown for cultures established with cells from an HIV-negative (circles) and an HIV-infected individual (squares). (C) ELISpot assays. CD8+ cells from an uninfected donor (upper row) and an HIV-infected donor (lower row) were placed into the wells of an IFN-α (multisubtype) ELISpot plate. Shown are digital images of wells containing 50,000 HIV-1-infected CD4+ cells cultured alone (column 1), 250,000 CD8+ cells cultured alone (column 2), or CD8+ cells that were cocultured at a 5:1 ratio with HIV-1-infected CD4+ cells (column 3). The ELISpot plates were processed after 24 h of cell culture. The results are representative of 3 independent experiments.