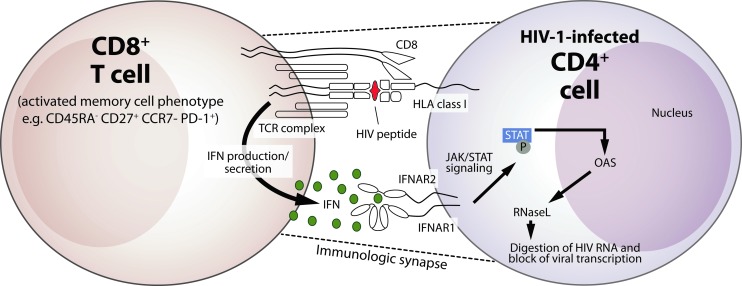
FIG. 8.
Proposed mechanism for the CD8+-cell-mediated suppression of HIV-1 replication. Illustrated is a model for the CD8+ cell noncytotoxic anti-HIV response (CNAR). Upon recognition of a cognate antigen presented in the context of HLA class I by HIV-1-infected CD4+ T cells, a signal is transduced via the T cell receptor (TCR) complex on memory CD8+ T cells (Killian and others 2011) that elicit the secretion of type I IFN. The secreted IFN binds to the IFN receptor (IFNAR2) on the CD4+ target cell, and the subsequent interaction with IFNAR1 activates the JAK/STAT pathway and promotes the phosphorylation of STAT1 and STAT3. This activity induces the upregulation of multiple IFN-responsive genes, including 2′,5′-oligoadenylate synthetase (OAS) and ribonuclease L (RNase L), which can have downstream inhibitory effects on HIV-1 transcription and virus replication.